MindMap Gallery Weaknesses of Weimar government
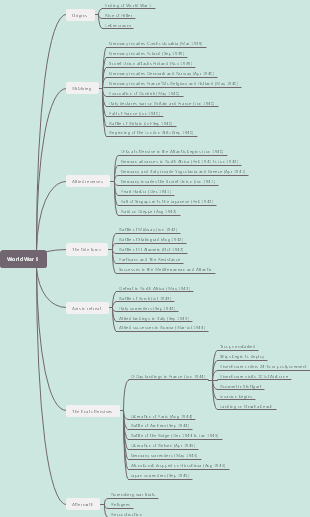
Weaknesses of Weimar government
This history mind map explains the political, economic, and social challenges that the Weimar government faced.
Edited at 2021-07-12 09:05:14Weaknesses of Weimar government
- Recommended to you
- Outline