What is a Concept Map: Definition, Benefits, and How to Create One
Concept mapping is a great tool for analysis as it’s a technique that places emphasis on illustrating how concepts are linked and related. This article has elaborated on the benefits of concept mapping.
Edraw Content Team
Create Mind Maps Today!
EdrawMind is a mind mapping tool equipped with 700+ cliparts. This article presents a step-by-step guide to creating a creative mind map to present your idea elegantly. Try EdrawMind and create hundreds of mind maps today!
1. What is a Concept Map?
Imagine having a large body of data and information that you need to structure and present in a way that your audience can easily connect to, understand, and, most importantly, remember. Giving information in just plain text often comes across as dull, and such presentations will end up becoming wearying, flat sessions that, for the most part, remain forgettable to the audience.
But you can avoid being that person who presents information in long boring lines of text when you understand what a concept map is.
So what is a Concept Map? A concept map is a diagram that depicts information, ideas, and concepts in a graphical format. Concept maps are high for structuring and organizing information because in concept mapping, the information is displayed hierarchically, and the relationships that exist between concepts that are traced and depicted using lines or arrows.

2. What Should a Concept Map Include?
To derive the full value that concept maps offer, it is important to note the key features that set concept maps apart from other organizational diagram tools. Understanding what each feature represents will help you create a concept map that is both effective and well-structured. The features are outlined below:
- Focus question: Why are you creating a concept map? What problem does your concept map solve? What issue does your concept map address? These questions are essential to ask because they give focus to the concept map you want to create. A concept map cannot be created independent of a reason. Framing a focus question is a critical element of concept mapping because it makes clear from the outset what problem or challenge that is addressed in the concept map. Starting with a focus question provides guidance and context.
- Nodes: The nodes are the most prominent feature of concept maps. Nodes are represented by either circles or boxes and usually enclose a concept or idea. Think of nodes as the containers for concepts. Nodes are ordered in a hierarchical format, and relationships between nodes are depicted using linking lines or arrows.
- Cross-links: Concept maps analyze and show how concepts and ideas are interrelated and these relationships between concepts are illustrated using cross-links.
- Linking words: Linking words, sometimes phrases, are the words that appear on the line connecting two concepts. These linking words are used to specify the kind of relationship that exists between concepts.
- Hierarchical Structure: More often, concept maps are constructed in a hierarchical fashion. This means that the broader and more general concepts come first and are placed somewhat at the top of the map, while concepts that are narrower and more specific are placed below. As a result of this hierarchical structure, the information presented in a concept map usually takes a downward flow, going from top to bottom.
- Propositional Structure: Recall that the linking words/phrases describe the type of relationship between concepts. The propositional structure of concept maps is illustrated in how the linking words connect two concepts. To understand the propositional structure, form a proposition statement from two concepts and the linking word that connects them. The proposition statement follows the format: concept-linking word/phrase-concept.
3. Benefits of Using Concept Maps
Concept maps enable you to gain broad insight on a subject and visualize the relationships between ideas and concepts.
Concept maps are useful for analyzing big data or a large body of information because they break up information into smaller chunks, going from broad to specifics.
Concept maps are useful for integrating new knowledge and information with already existing knowledge, thereby improving learning.
Concept maps are especially helpful for visual learners, enabling them to develop a firm grasp of concepts that would otherwise be difficult with only text.
Concept maps have been proven to improve learning and enhance the brain's ability to retain information.
The use of concept maps enables one to develop metacognitive and advanced-thinking skills.
Concept maps are useful for distilling complex information into small, understandable bits, fostering a holistic understanding of an idea or subject matter.
Concept mapping employs the use of both sides of the brain, thereby fostering strong analytical skills and creativity.
4. Concept Maps in Science, Education, and Business
Owing to the versatility of concept maps and the benefits that can be derived from concept mapping, several fields have employed the use of this essential technique. Highlighted below are some means by which concept maps can be applied in science, education, and business.
4.1 Concept Maps used in Science
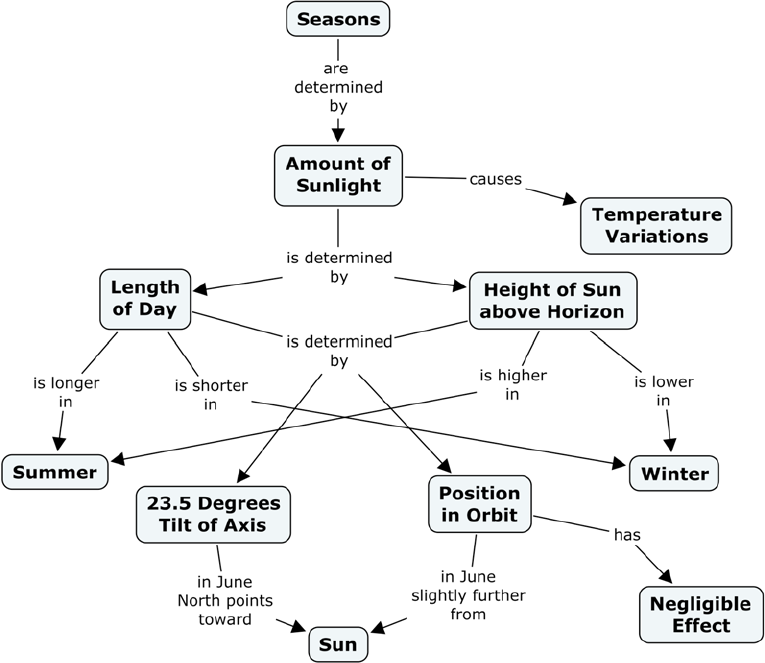
The use of concept maps first originated in science, in 1972, among a group of researchers conducting a study to understand the variations in how children absorbed science concepts. The study produced a vast amount of data that the researchers found it difficult to structure their research and gain meaningful insights. It led to the development of concept maps, a better way for the researchers to structure and present the information derived from their scientific studies.
And today, concept maps remain an extremely vital tool in the area of scientific research. Scientists employ the use of concept maps to better organize and visualize the results of their research. Concept maps enable science researchers to make sense of the data derived from their studies, draw up meaningful interpretations, and identify the patterns and relationships that exist between bodies of knowledge.
Scientific research and studies involve a great deal of analysis and evaluation. Researchers have now utilized concept maps as an evaluation tool to assess the significance and validity of ideas that they are investigating.
4.2 Concept Maps used in Education
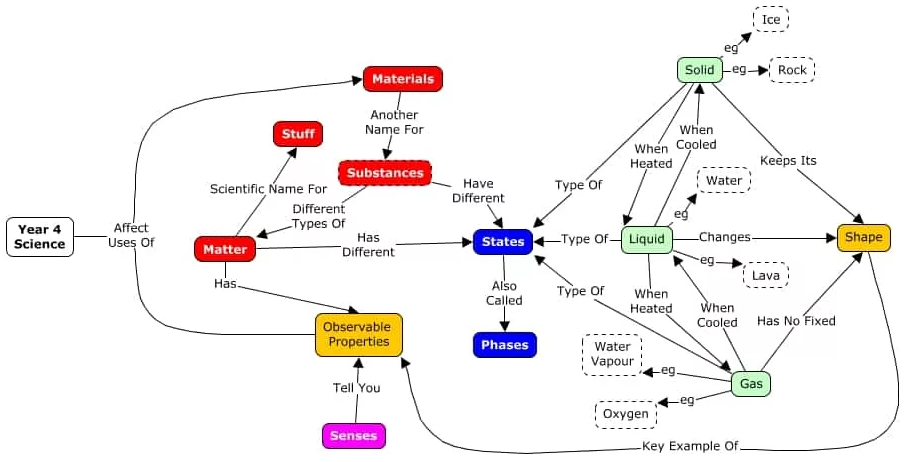
There is research-based evidence that shows the efficacy of concept mapping as a learning aid in the field of education. More and more educators and teachers are finding concept maps to be an invaluable tool for passing across knowledge to their students.
Concept maps are structured to suit how the human brain processes and absorbs information and new knowledge. The brain absorbs and stores information in a structured format, linking together interrelated pieces of information. Thus, when concept maps are employed as a tool for education, students are more likely to assimilate new knowledge and form meaningful connections between old and new knowledge.
Concept maps in education foster deep comprehension among students because it enables them to identify how concepts are related, thereby deepening their understanding about a subject matter.
Concept maps are structured to incorporate visual elements, and educators have found this to enhance visual thinking among students, enabling them to retain more information as opposed to when learning methods are restricted to text only.
4.3 Concept Maps used in Business
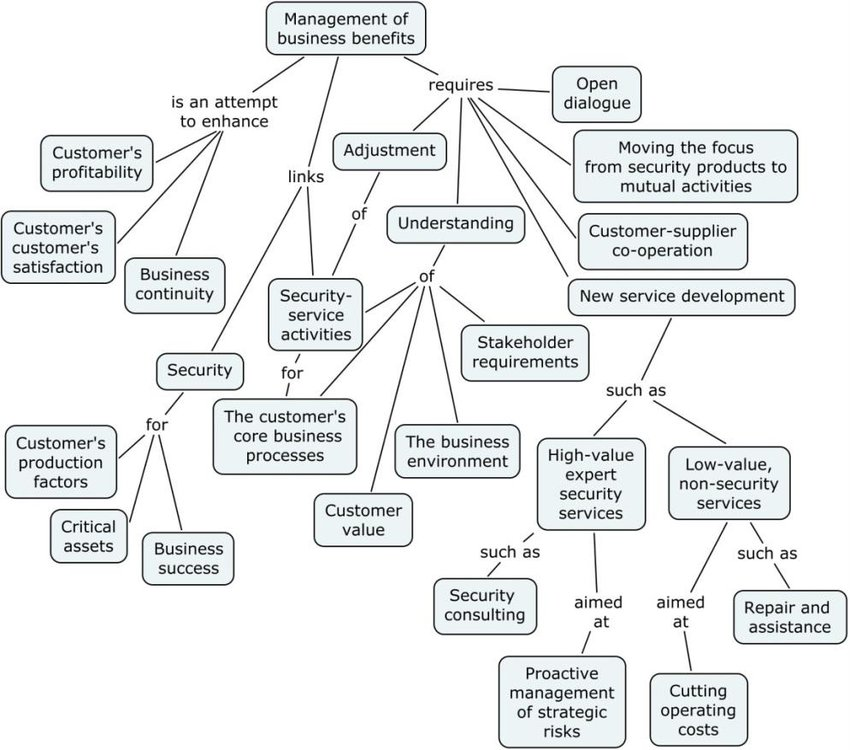
Concept maps have also found application in the business world as an aid for proper business analysis. Businesses can employ the use of concept maps to explain their business model, their work, or the design process. They can also leverage on the propositional structure of concept maps to illustrate how the parts of their business process connect and flow together. Concept maps can also be used in business to depict and manage operational workflow and tasks.
# Mindmeister
Mindmeister is an intuitive mind mapping software that is suitable for both individuals and teams. It offers a user-friendly interface that allows users to create mind maps quickly and easily. Mindmeister also provides collaboration and sharing features that enable teams to work together in real-time. Some of the notable features of Mindmeister are presentation mode, task management, and notes section. It is available as a web-based application and mobile app for Android and iOS.
# Mindmup
Mindmup is a web-based mind mapping tool that is free to use. It offers a simple and clean interface that is perfect for creating basic mind maps. Mindmup also provides integration with Google Drive and Dropbox, which allows users to store and share their mind maps easily. Some of the notable features of Mindmup are collaboration and sharing, presentation mode, and the ability to export mind maps as images, PDFs, or HTML files.
5. How to Make a Concept Map
To create a concept map, keep the structure and underlying principle of concept mapping in mind. The structure here will refer to the hierarchical nature of concept maps. In contrast, the underlying principle will be the fact that concept mapping is primarily about depicting the relationships that exist between ideas and concepts. With that in mind, you are set to produce a good concept map.
Step1 Decide whether to draw a concept mind by hand or by software
Concept maps can be illustrated by hand or by using a concept mapping software. Drawing a concept map by hand usually presents some limitations, but this can be avoided by using concept mapping software like EdrawMind.
EdrawMind is an intuitive, beginner-friendly mapping tool that is available across all platforms and syncs between PC, Web, and mobile devices. You can sign up for a free account and access your content map across all platforms without limitations.
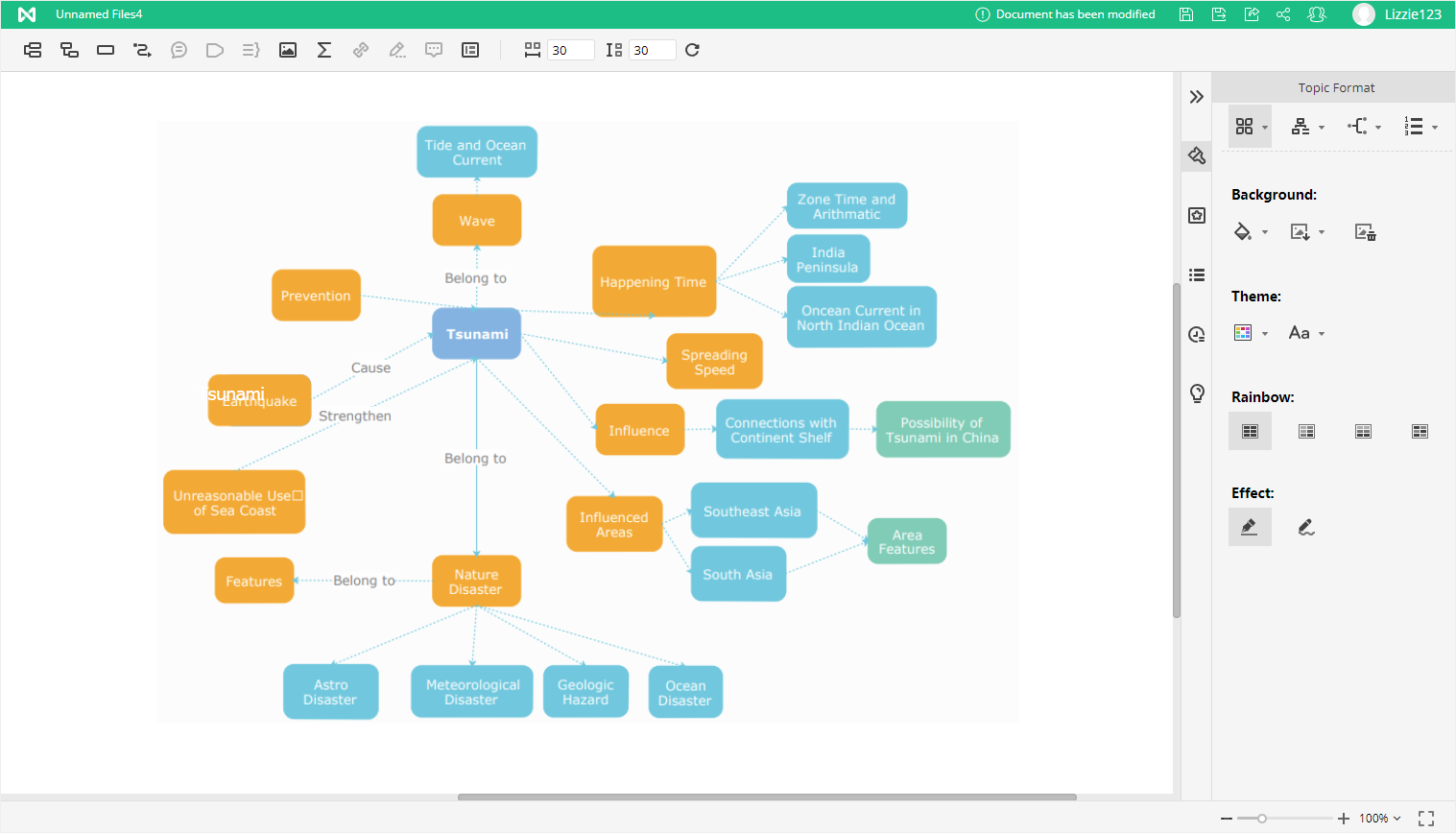
Step2 Decide on a main topic using a focus question
As earlier explained in this article, a focus question helps to guide and give context to the content map being created. Frame a focus question to come up with the issue or problem that you'll like your concept map to address. The main topic will be the core of your concept map and will be further broken done into smaller parts to illustrate the relationships that exist between ideas.
Step3 Figure out the key concepts associated with your main topic
Think of the main topic as the 'parent' and the key concepts as the 'children'. Think deeply about your main topic to determine those concepts that are easily associated with your main topic. Once you have determined the key concepts, order them in a hierarchical fashion, going from the most general to the most specific.
Step4 Illustrate the relationships between concepts
Depict concepts that are related by connecting them with linking words/phrases. Use crosslinks to illustrate the relationships between concepts in different domains. Keep refining the map until you run out of thoughts and exhaust all relationships.
Concept maps provide us with a broad perspective of a subject matter, enabling us to see the big picture to draw up meaningful interpretations. Concept mapping is an excellent tool for analysis because it's a technique that emphasizes illustrating how concepts are linked and related - understanding how concepts are connected in a critical approach for deepening our comprehension of a subject matter.

How to Make a Concept Map
Unlock your creativity and enhance your learning with a simple yet effective tool - learn how to make a concept map today!