MindMap Gallery Geography of Canada
- 450
- 2
- 1
Geography of Canada
This is a mind map talking about the Geography of Canada. You can create a mind map like this effortlessly.
Edited at 2020-09-28 12:04:21- Creative Halloween Costume Ideas
Halloween has many faces. The theme you envision should influence how you decorate the party space. Jack-o'-lanterns and friendly ghosts are more lighthearted Halloween characters. Zombies, witches, and vampires are much darker. If you want to celebrate all the fun sides of Halloween, then it’s okay to mesh the cute with the frightening. Here is a mind map which lists down the 39 Cutest Couples Halloween Costumes of 2021.
- 35 Best and Classic Halloween Movies
Halloween simply wouldn't be Halloween without the movies that go along with it. There's nothing like a movie night filled with all the greatest chainsaw-wielding, spell-binding, hair-raising flicks to get you in the spooky season spirit. So, break out the stash of extra candy, turn off all the lights, lock every last door, and settle in for the best of the best Halloween movies. Here are the 35 Halloween movies listed on the mind map based on the year of release.
- Halloween Party Ideas Mind Map
This mind map contains lots of interesting Halloween trivia, great tips for costumes and parties (including food, music, and drinks) and much more. It talks about the perfect Halloween night. Each step has been broken down into smaller steps to understand and plan better. Anybody can understand this Halloween mind map just by looking at it. It gives us full story of what is planned and how it is executed.
Geography of Canada
- Creative Halloween Costume Ideas
Halloween has many faces. The theme you envision should influence how you decorate the party space. Jack-o'-lanterns and friendly ghosts are more lighthearted Halloween characters. Zombies, witches, and vampires are much darker. If you want to celebrate all the fun sides of Halloween, then it’s okay to mesh the cute with the frightening. Here is a mind map which lists down the 39 Cutest Couples Halloween Costumes of 2021.
- 35 Best and Classic Halloween Movies
Halloween simply wouldn't be Halloween without the movies that go along with it. There's nothing like a movie night filled with all the greatest chainsaw-wielding, spell-binding, hair-raising flicks to get you in the spooky season spirit. So, break out the stash of extra candy, turn off all the lights, lock every last door, and settle in for the best of the best Halloween movies. Here are the 35 Halloween movies listed on the mind map based on the year of release.
- Halloween Party Ideas Mind Map
This mind map contains lots of interesting Halloween trivia, great tips for costumes and parties (including food, music, and drinks) and much more. It talks about the perfect Halloween night. Each step has been broken down into smaller steps to understand and plan better. Anybody can understand this Halloween mind map just by looking at it. It gives us full story of what is planned and how it is executed.
- Recommended to you
- Outline
Geography of Canada
International Interconnections
Canada: international teamplayer
Canada is importantinternationally
seen as compassionate and caring
commonwealth: former British colonies
25% of world's population
south Africa, Canada, India
family connections
United Nations
formed after WWII
there are 192 countries
conflict resolution, peacekeeping, diplomacy
other organizations: UNESCO, UNICEF,
NATO (north Atlantic Treaty Association), WorldBank, NGO's
Imports/ Exports
Trade is all about exchanging goods andservices
Importing is all about bringing in goods fromforeign places; exporting is giving goods toforeign places
Importing gives use things we cannot grow ormanufacture in Canada; exporting gives us $$$
Canada exports raw materials, auto mobiles,airplanes, nuclear products
80% of our exports are to USA
Trade surplus
fair trade vs. Protectionism
NAFTA( North American Free Trade Act) Wehave free trade with Mexico and USA
Tariff, Quota, Subsidy, all forms of protectionism
GDP ( gross Domestic Product) measures acountry's worth.
Canada's GDP was 1.57trillion
some companies make more than mostcountries' GDP's they have more power
JP Morgan Chase Bank ( #1 company in theworld)
Globalization
the world is a global village and everyone isconnected
6th degree of separation ( we are related by 6people)
cultural awareness vs. cultural exploitation
Quality of Life
world heritage sites
one in Quebec city
GDP shows standard ofliving
developed, developing, industrialized
UNESCO ( United Nations Educational,Scientific and cultural Organization)
What's aCanadian?
does Canada have culture or are we Americanwannabe's?
Do stereotypes define us?
International policies
First Aid: Helping developing countries who needsupport (myth in sorts)
Donated 0.285 of its GDP
Peace Keeping: Lester B. Pearson, A force toavoid conflict
Syria conflict
Human Rights: Fighting for the rights of people
Lloyd Axelworthy
People on the land
Industries
four types of industries
Primary
agriculture
secondary
manufacturing
tertiary
most people work in this industry; service
researching
researching
refers to particular types of labour that are done
entrepreneurs are people who run their ownbusinesses
education has nothing to do with the levels ofindustry
work
this is important for Canadianlife
unemployment happens for many reasons;laziness is very uncommon
under employed
single mothers, visible minorities and loweducation are mos likely to be umemployed
employment is affected by the cost of operating abusiness
often relocate to lower costs
working poor; those who work, but cannot affordbasic needs
volunteering; people who work for free
single industry towns
resources
many companies are lured by Canadaèsresources
resources are the base of materials
a resourceis anythingfound innaturethat is ofvalue
non renewable resources
operate in geologic time
renewable resources
operate in human time
flow resources
operate in the momentfouund
capitalist vs.environmentalist
money vs. the earth
environmentalist: we are the world
capitalist: money$$$$
fishing
Pacific, Atlantic, freshwater
The Atlantic fishery collapsed because ofoverfishing.
find cod,herring there.
destructive fishing practices
lots of fish because of the shallow waters
pacific fisheries fear that theywill collapselike theAtlantic
fish found: salmon!!
salmon are caught on their migration routes
Freshwaterfisheriesare aroundthe greatlakes area
Lake Erie the most profitable lake; shallowwaters
sport fishing= $$$
Effluent
three groups fighting for control of fisheries:Commercial, sport, Native
agriculture
if you ate today, thank a farmer
1 in 5 jobs are related to agriculture
farming is based off of chance
growing season is above 5*C
extensive and intensive farming
intensive farming; small land, high valueperishable's foods with more workers and fewequipment
degradation of farmland: erosion, overuse
extensive farming is large land, non perishable foods with lotsof equipment
in the 1880s 80% of Canadians were farmers,now less than 3%
Niagara fruitbelt
forestry
10% of worlds forests inCanada
almost 1/2 of Canada is forests
two basic types of wood; softwood andhardwood
softwood lumber makes pulp and paper
hardwood lumber makes planks and lumber
big tree become lumber and small trees makepulp and paper
the industry creates a lot of money ($22 billion)
high value of wood caused clear cuttingpractices
over consumption threatensthe forestry industry at everylevel.
RECYCLING!!
mining
everything in our lives has todo with mining
mining produces the highmultiplier effect; where themore you process it, thehigher value there is.
a mineral is a naturallyoccurring pure chemicalcompound( includingelements)
four types
industrial minerals; diamonds
metallic minerals; gold
structural minerals; gravol
fuel minerals; coal
types of mining
open pit mining; for mineralsnear the edge then go lowerin the Earth
strip mining; for mineralsclose to the surface of the Earth
underground mining; forminerals further in the earth;most dangerous
energy
Canada is one of the topenergy users in the world
non renewable and renewableresources.
Canada has fossil fuels,hydrocarbons, hydroelectricity and nuclear
hydroelectric energy needs a slope and water
Ontario is the largest user of Nuclear energy inCanada.
it is cheap, clean energy.
coal used to be popular, but it causes toomuch pollution
most of our coal comes from Alberta
OIL!!!
it is found underwater too, but very difficult toextract
also in the North, too expensive to bother...fornow
Tar sands are mucky areas of sand mixedwith oil.
greenhouse gases trap heat to the Earth.
global warming; climate change
carbon oxygen cycle
Natural gas usually found above oil, but it verytemperamental; use with caution
good for home heating, used in power plantsto generate electricity
carbon footprint
Average Canadian footprint is 8 hectares
figure out how much space we need to liveour lives
transportation
transportation of goods that are not availablein different areas.
highway 401 is the largest highway inNorth America
Cars are the most popular form oftransportation for Canadians
four major waterway; Hudson bay, greatlakes, Pacific Ocean, Atlantic Ocean.
Canada's Cultural Diversity
population
population is the number of people wholive in a given area at a given time.
population is dynamic
population density
this is the meausre of the number ofpeople who live in a standardized area.
Canada's population density is 3.1 peopleper km2.
four factors
birth rate, death rate, immigration,emigration
birth rate the amount of babies born in apopulation. Usually written in a rate per 1000people.
death rate is the amount of people who die ina population. It is usually written as a rate per1000 people.
immigration iswhen peoplemove fromone country toanother.
Emigration is when people move out of acountry to another.
calculating natural increase: birth rate deathrate
cloropleth mapping.
using colour shades to represent an amountof something using 36 different classes.
can only use one colour (moncromatic)
settlement
Ecumene: where the population lives. Thisis the Windsor Quebec city corridor
different types of settlements.
hamlet, village, town, city, megacity, CMA,megatopolis...
census: statsCanada.
demography is the study ofpopulationtrends.
rates can be shown as a percentage
agesex pyramids
shows population patterns.
Divides the population by age and bygender
males on the left, females on the right
dependency load
15 and under and 65 and over
they take up appropriately 1/3 of Canada'spopulation.
BABY BOOMERS!!
from 19451960, more babies thanexpected were born.
this cold be because the war was over,soldiers came home to a safeenvironment.
flow maps
uses arrows and colours to showimportance.
the bigger the symbol,the more important itis.
the fatter the arrow, the more important itis.
immigration
people immigrate fro many reasons
push + pull factors
Some factors are: war, education,prosecution, refuge etc...
push factors are what make you want toleave a country
pull factors are what attract you to anothercountry
how to get intoCanada:
if you have a health issue or a criminalrecord, there's a very slim to none chance ofgetting in.
different classes to apply into:
skilled workers class
people with education and work experiencethat can help them find a job and help theeconomy
investors
people who are going to put money toCanada.
Provincial nominees
provinces can nominate someone who hasapplied to work in a specific field in theirprovince.
family
You can bring siblings, parents,grandparents, children, commonlawpartners, spouses, nephews, nieces andgrandchildren.
refugee
you can only apply under this class if youhave proof that you are not safe in yourcountry.
currently you need a minimum of 67 of the100 points to get inon the test.
education is the highest category on the test.
multiculturalism... amyth?
a policy that encourages cultural diversityand respect
there are ethnic enclaves in Canada (GreekTown)
tossed salad vs. melting pot
assimilation
cultural imprints
social imprints
the ways that people behave
language, religion, family traditions, clothing,food, sports
physical imprints
The ways people affect their surroundings
Architectures,specialityshops,restaurants.
urban settlements
breaking up the land
"Long lot" system
section system
line+ concessions system
over 90% of Canadians live in urban areas.
there are transportation cities, manufacturingcities, resource cities, service cities
many ways to use the land
residential
housing
Institutional + public buildings
schools, libraries
transportation
roads, highways, parking lots
Open space
parks
Industrial
stores, factories
commercial landuse; meant for buying andselling goods only
Low order, middle order, high order types ofstores
big cities
Alienation
feeling alone among thousands ofpeople
poverty
cost of living is higher
crime
more people+ more crime
physical blight
functional blight
areas that cannot be used for their originalpurpose
frictionalblight
this is when there is conflicting landuse
deterioration of landscape.
Urban fringe
mixed land use
Indigenous people
also known as first nations
often tried to be destroyed for the land byEuropeans
colonize, kill, residential schools
us vs. them
Canada's physical diversity
Earth
4.6 billion years old
possibly formed by a meteor
oblete spheroid
third planet from the sun
looks like a large blue and green ball fromspace
Different parts of the Earth
Mantle
The liquidy area just under the crust andabove the core.
lava; magma
core
the centre of the earth.
crust
the hard outside layer of the Earth; whatwe see.
systems
a group of different parts that connect to makea whole
Human systems
Communication systems, transportationsystems, information systems etc...
Natural systems
Ecosystems
Macro systems
Hydrosphere
What makes a natural system?
displays synergy
supports all living things
are driven by energy from the sun
are connected to one another in complexrelationships
decomposes and recycles all waste
are affected natural and human influence
are not well understood by humans
operate on very long timelines
use all four spheres
synergy
when the sum has more value than the parts
Physical regions
There are seven landform regions.
3 highland
Appalachian
Cordillera
Inutian Mountains
3 lowlands
Hudson Bay lowlands
Great lakes/ St.Lawrence lowlands.
Interior plains.
CanadianShield.
Soil
4 components
air, soil, water and humus (dead stuff)
layers:Dead leaves, A horizon humus layer, B horizon subsoil, Bedrock, Parentmaterial.
Podzols are found in forests with deciduoustrees.
chernozems are thick grassland areas thatcover large areas of the prairies.
flora is plant life
fauna is animal life.
Plate tectonics
in 1915, Alfred Weigner came up withcontinental drift. He noticed how the earthlooked like a big puzzle.
Evidence: Geologic fit
Fossil evidence
Geologic match
In 1960's J. Tuzo Wilson came up withPlate tectonics. This is where the Earth ison plates that are moving away from eachother slowly.
Earthquakes and ocean ridges occur whentwo plates and passing one another. Theyscrape or they overlap causing damage.
You get volcanoes when the plates aremoving away and mountains when theymove together.
Era
4 geologic eras
Pre Cambrian era
oldest and longest era. The Canadianshield was being formed. Mostly igneousrock being found. Shield worn down byerosion and first single cell organisms.
Paleozoic
Age of the invertebrates. Plates begin tocollide. The Appalachian mountains areforming. 375 million years long.
Mesozoic
Age of the reptiles. Birds and mammalsappear. Western cordillera forming.
Cenozoic
Age of the hominids( humans) Most ofCanada covered in glaciers. Formed mostof Canada today.
BLOWER
Bodies of Water
Water moderatestemperature
Lake effect snow
Latitude (temperature)
further from the equator, cooler thetemperature.
albedo
Ocean current
water does not change temperature asquickly as air does.The water temperaturewill have an affect on the areas surroundingthem.
currents travelling to equator are are coolerand currents travelling away from equatorare warm.
Relief/ Landforms
moist air forced up a mountain can result inprecipitation.
on the other side there's dry air.
Wind/Air masses
air moves in large volumes called airmasses
temperature and moisture of air massesdepend on their origination.
JET STREAM
Elevation/ Altitude
Air mass edges are called fronts
air altitude increases temperaturedecreases.
Macro spheres
hydrosphere
All of the Earth's water in it's solid, liquidand gas forms
biosphere
The area inside the earth where life canexist
lithosphere
The earth's outer layer of rock
atmosphere
All of the earth's gases.
Convection
When convection pushes the crusttogether you get mountains. (itcompresses and folds)
When convection pulls the crust apart itforms cracks. (valleys). A fault appearscausing earthquakes.
When two faults appear at the same time,it causes a rift valley.
There is a rift valley between Ottawa andthe New York state.
Erosion is the wearing down of something.Wind, water ice and gravity are factors oferosion.
the debris is moved somewhere else bynature. (desposition)
a mound of debris in between twoglaciers is called a moraine. ( there isone in Oakville)
glaciers are overgrown land icebergs. Theygrow shrink and move.
When they move they scrape the land ofvegetation, minerals, rocks, soil and depositit somewhere else.
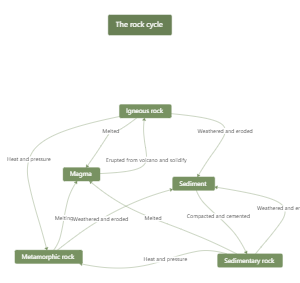
Rocks
three types of rocks
igrneous
pumice
Intrusive
this is when the rock cools inside the earth.
extrusive
this is when the rock cools outside of theEarth.
made from magma inside t he Earth andthen cooled inside or outside of the earth.
metamorphic
slate
It is a mixture of both rocks;hence the namemetamorphic.
sedimentary
sandstone
made from sediments under the sea
Are all formed in neverending cycle. Itcould be a web because you can go fromone point to another easily.
Climate vs weather
what is weather/
weather is what ishappening at a specifictime.
what is climate?
climate is the patternsthat are watched overalong period of time (100years).
climate is regular whileweather can beunpredictable.
factors that affect both:
temperature andprecipitation.
frontal precipitation.
when 2 fronts meet.
The warm front is pushed over the coldfront. As air rises and cools its condensesinto water droplets. Eventually precipitationoccurs.
orographic precipitation.
wind, water vapour, rises, cools, condenses,clouds form, rain falls, yay orographic!
convectional precipitation.
As the earth's surface is warmed, warm airrises, cools and causes condensation.Eventually heavy down occurs.
Happens in continental areas.
vegetaition
a biome is a large region on Earth
Thee boreal is the largest biome in theworld.
Deciduous trees 63% of Canadianforests
coniferous trees 22%
mixed the rest
Geography, Canada and Me
What is geography?
geography is the study of the Earth, itslandforms, its resources and processes, thepeople who live in the Earth and theirconnection to the environment.
Geography is the study of the Earth
Three themes of Geography
Human geography
Physical geography
Geomatics
5 themes of geography
The world in spatial terms (location)
Focuses on the question where?
Where is it? How can I get there?
places and regions
each place has certain characteristics to them
How can we break up the different areas ofCanada?
change
Everything changes, either slowly or quickly
Why is this change happening? what can wedo with it?
connections and interconnections
Everything is connected in some way
We rely on systems and systems rely on us.We are not whole unless everything is alright.
Environment and society
Without environment, there is no society.Without society, there is no environment. Weneed each other to survive.
Cardinal directions
directions are important for our way of life
16 pointcompassrose
Bearing system
Uses both numbers and directions. (N*0)
Azimuth system
just uses numbers
local location
6 figure military grid
accurate to 100m
UTM
alphanumeric grid
easy to use, but not very accurate
uses both numbers and letters
Time zones
Canada has 6 time zones.
that's about half of Russia!
Greenwich, ENG
0
Provinces and territories
capitals + Provinces
all 13
"Over Canada"
Peggy's cove
Niagara falls
What is a map?
A map is a 2D representation offeatures on the Earth.
Topographic maps
Longitude + Latitude
Thematic maps
New node
The study of maps is called cartography
12 cartographic guildlines
Scale
5 types of scale.
Graphical scale
New node
Word Scale
Representativeratio
Not to scale
Scale unkown
Contour lines
They show elevation on a map.
Rules:
1. They never touch or overlap
2. they are continuous
3. The closer the contour lines, the steeper theland.