MindMap Gallery 3.6 Learning and learning theories
- 83
3.6 Learning and learning theories
This is a mind map about learning and learning theories. The main contents include: humanistic learning theory, constructivist learning theory, cognitive learning theory, overview of learning, and connective learning theory (behaviorism).
Edited at 2024-04-12 22:18:56- Valentine's Day marketing campaign
This Valentine's Day brand marketing handbook provides businesses with five practical models, covering everything from creating offline experiences to driving online engagement. Whether you're a shopping mall, restaurant, or online brand, you'll find a suitable strategy: each model includes clear objectives and industry-specific guidelines, helping brands transform traffic into real sales and lasting emotional connections during this romantic season.
- 30 Creative Ideas for Valentine's Day
This Valentine's Day map illustrates love through 30 romantic possibilities, from the vintage charm of "handwritten love letters" to the urban landscape of "rooftop sunsets," from the tactile experience of a "pottery workshop" to the leisurely moments of "wine tasting at a vineyard"—offering a unique sense of occasion for every couple. Whether it's cozy, experiential, or luxurious, love always finds the most fitting expression. May you all find the perfect atmosphere for your love story.
- Milano Cortina 2026 Ice Hockey Schedule
The ice hockey schedule for the Milano Cortina 2026 Winter Olympics, featuring preliminary rounds, quarterfinals, and medal matches for both men's and women's tournaments from February 5–22. All game times are listed in Eastern Standard Time (EST).
3.6 Learning and learning theories
- Valentine's Day marketing campaign
This Valentine's Day brand marketing handbook provides businesses with five practical models, covering everything from creating offline experiences to driving online engagement. Whether you're a shopping mall, restaurant, or online brand, you'll find a suitable strategy: each model includes clear objectives and industry-specific guidelines, helping brands transform traffic into real sales and lasting emotional connections during this romantic season.
- 30 Creative Ideas for Valentine's Day
This Valentine's Day map illustrates love through 30 romantic possibilities, from the vintage charm of "handwritten love letters" to the urban landscape of "rooftop sunsets," from the tactile experience of a "pottery workshop" to the leisurely moments of "wine tasting at a vineyard"—offering a unique sense of occasion for every couple. Whether it's cozy, experiential, or luxurious, love always finds the most fitting expression. May you all find the perfect atmosphere for your love story.
- Milano Cortina 2026 Ice Hockey Schedule
The ice hockey schedule for the Milano Cortina 2026 Winter Olympics, featuring preliminary rounds, quarterfinals, and medal matches for both men's and women's tournaments from February 5–22. All game times are listed in Eastern Standard Time (EST).
- Recommended to you
- Outline
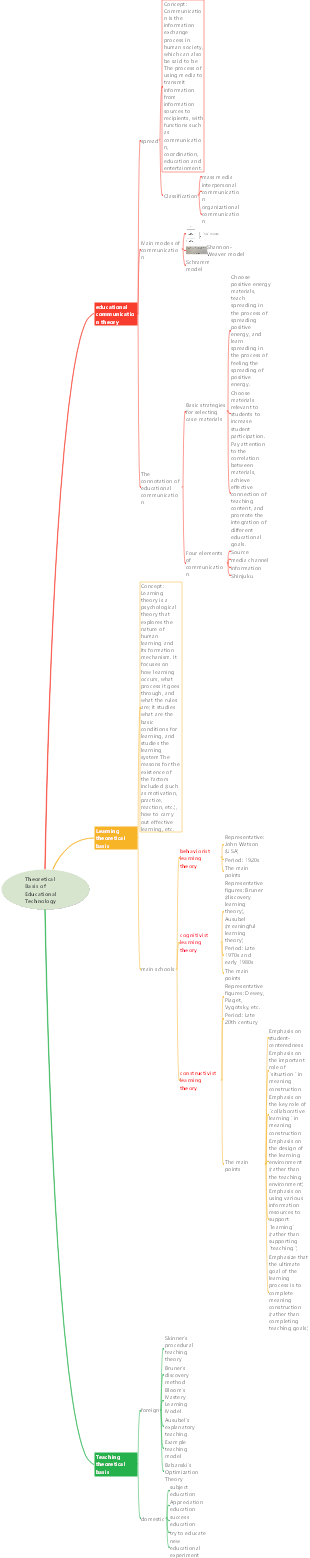
Learning and Learning Theory
Overview of learning
Definition of learning
Broad learning: Long-lasting changes in an individual’s behavior or behavioral potential resulting from practice or repeated experience in a specific situation
There must be changes
Changes are relatively permanent
Repeated experience (practice)
Manifest changes Potential changes
Learning in the narrow sense: learning by humans or students
Students' learning is mainly aimed at mastering existing indirect experience
Classification of learning
Classification by learning results (Gagne)
verbal message
what is
Intelligence skills
How to do it
cognitive strategies
Attention, learning, memory, thinking and problem solving
manner
Motor skills
From Learning Nature and Form (Ausubel)
how learning takes place
accept learning
discovery learning
The relationship between learning materials and original knowledge
machine learning
meaning learning
Most important: meaningful acceptance of learning
In terms of learning content
knowledge learning
Skill learning
learning social norms
First tasks: Dual bases - basic knowledge and basic skills
According to the existence form and complexity of knowledge itself
Symbolic learning (representational learning; representation learning)
concept learning
Grasp the common essential attributes and key characteristics of a type of things
proposition learning
Proposition is the smallest unit of knowledge
Obtain the composite meaning of a proposition composed of several concepts
Used to state general rules, distances, laws, formulas, etc.
Connective Learning Theory (Behaviorism)
Thorndike's Trial - Trial and Error Theory (Learning Rules)
Classic Experiment: Hungry Cat in the Cage Experiment
learning rules
law of effect
practice law
preparatory law
Students with favorable conditions are not motivated to learn
Thorndike - "the father of modern educational psychology", the founder of scientific educational psychology, and the first psychologist to systematically discuss educational psychology
Viewpoint: Define learning as the connection between stimulus and response (S-R) without the need for an intermediary
Pavlovian-classical conditioning (generalization and differentiation)
Classic experiment: secretion of digestive glands in dogs
Basic laws of classical conditioning
Gain and fade
Conditioned stimulus - ringtone; unconditioned stimulus - meat
Generalization and differentiation
Generalization: response to similarities between things
Differentiation: response to differences in things
Bravery and recklessness; humility and retreat
The stimulus occurs before the response. The stimulus occurs before the response.
Skinner-operant conditioning (reinforcement and punishment)
There are two types of behavior between humans and animals
responsive behavior
Pupil constriction when exposed to bright light
operant behavior
Rewards and Punishments
Skinner proposed the reinforcement theory
Viewpoint: The essence of learning is to establish the connection between the operation and the reinforcer
Basic laws of operant conditioning
strengthen
Positive reinforcement (implementation rewards)
Negative reinforcement (withdrawal of punishment)
Increase the frequency of behavior
subside
punish
Positive punishment (giving unpleasant stimulation)
Negative punishment (withdrawal of pleasant stimulation)
Reduce the frequency of behavior
Stimulus occurs after reaction
Application of Operant Conditioning Theory in Education: Programmed Teaching and Teaching Machines
Principles of program teaching
small steps
positive reaction
self-paced
Timely feedback
Reduce error rate
Bandura-Social Learning Theory (Three Sources of Motivation)
division of learning
Participatory learning: learning by doing
Vicarious Learning: Observational Learning
Three sources of motivation
direct reinforcement
vicarious reinforcement
Reinforced by role models
self-reinforcement
reward yourself
It is believed that observational learning is the most important form of human learning, including four sub-processes
Notice
Keep
Reappear
motivation
Vicarious reinforcement occurs during this stage
Example: Kill one person as a warning to others
cognitive learning theory
early cognitive learning theory
Koller: Gestalt Gestalt - Epiphany Theory
Learning Outcome: Learning is not about stimulus-response connections, but about the formation of new Gestalts
Learning process: epiphany of situation
Consciousness is the intermediary between stimulus and response
organization between stimulus and response
representative figure
Wertheimer
Koler
Kafka
Tolman: Cognitive Map Theory (Symbolic Learning Theory)
Classic experiment: training a mouse to walk in a maze
The main points
The essence of learning: the process of S-O-R, resulting in the formation of a "cognitive map"
Learning process: forming a cognitive structure in which "goal-object-means" are linked together
Learning outcome: Comprehension of the overall situation
Cognitive learning theory believes that learning is the process of forming, enriching or reorganizing internal psychological structures, rather than the formation of stimulus-response connections or the strengthening or changing of behavioral habits.
Modern view of cognitive learning
Bruner's discovery learning theory
View of learning
The essence of learning: actively forming cognitive structures
Learning stages: acquisition, transformation and evaluation
The ultimate goal of learning is to build a good cognitive structure for students
Teaching concept
The purpose of education is to understand the basic structure of the subject
Master the teaching principles of the basic structure of the subject
motivation principle
structural principles
procedural principles
Strengthening principles
Ausubel's Theory of Meaningful Learning (Three Types of Assimilation)
two dimensions
according to the way learning takes place
accept learning
discovery learning
According to the relationship between learning materials and learners’ original knowledge structure
machine learning
meaning learning
Student learning is primarily about meaningful acceptance of learning
The essence of meaning learning: establishing a non-artificial and substantive connection between the new knowledge represented by symbols and the appropriate ideas already in the learner's cognitive structure
Conditions for meaning learning
objective factor
The learning materials themselves make logical sense
subjective conditions
Learners’ own factors
Have cognitive structures capable of assimilating new knowledge
Have a desire to learn
The internal psychological mechanism of meaningful learning—assimilation
Ausubel believes that the process of meaningful learning is the process of assimilation of new concepts by original concepts.
three relationships
Lower level learning (generic learning)
Derived generic learning
do not change
Related category learning
Change
The main difference between the two: whether the original concept has changed in its essential attributes
Upper level learning (overall learning)
learning in parallel
The result of meaningful learning is the formation of cognitive structures
Forerunner Organizational Technology (Ausubel)
Meaning: a kind of introductory material presented before the learning task itself, and its level of abstraction, generalization and synthesis is higher than that of the learning task
Example: Present the concepts of "metal" and "alloy" before learning the concept of "steel"; introduce background knowledge before learning a text
constructivist learning theory
The story of fish cow
The main points
constructivist view of knowledge
Knowledge is not an accurate representation of reality, nor is it the final answer, but only an explanation, a hypothesis
Knowledge cannot accurately summarize the laws of the world and cannot be used immediately. It must be recreated according to specific situations.
Understanding can only be constructed by students based on their own experiential background and depends on the learning process in a specific situation
Emphasis on the dynamic nature of knowledge
constructivist view of learning
active constructiveness
social interactivity
situational
constructivist view of students
Emphasize the richness and diversity of students’ world of experience
Emphasis on students' huge potential
“Students do not enter the classroom with empty heads.”
Teaching concept
Situational teaching (also called anchored teaching, problem situations, cooperative learning)
Cooperative learning
teaching implications
Use children's existing knowledge and experience as the growth point of new knowledge and guide children to grow new knowledge and experience from their original knowledge and experience.
Teaching is not the transfer of knowledge, but the processing and transformation of knowledge
Teaching is to enhance cooperation among students
anchored teaching
Allow learners to feel and experience real-life situations, rather than just listening to others introduce and explain the experience
scaffolded teaching
Build learning scaffolds
Personal constructivism (Piaget); social constructivism (Vygotsky)
humanistic learning theory
Maslow's learning theory
Maslow's hierarchy of needs theory
Only after lower-level needs are basically satisfied, higher-level needs will appear. (fully satisfied❌)
Rogers' humanistic learning theory
Humanism advocates a meaningful and free view of learning
learner self-involvement process
Learning is self-initiated by the learner
Learning is permeable
Learning outcomes are self-evaluated by learners
Student-centered teaching view (also known as "non-directive teaching model")
Teachers are not authorities, but "midwives" and "catalysts"
Informed and unified view of teaching goals
Rogers believed that human spiritual world includes two aspects: emotion and cognition.
The goal of education is to cultivate the "whole person"
Teaching objectives focus on process but not content (light on results)
Ranking of major schools of psychology
The first major force: behaviorism
The second largest force: psychoanalysis
The third major force: humanism
Non-guidance teaching is the teaching model of humanistic learning theory
Freezing the City Wall (Mobile Jie Cheng Qiang)