MindMap Gallery Frontier of Educational Technology Theory—Situated Cognition Theory
- 5
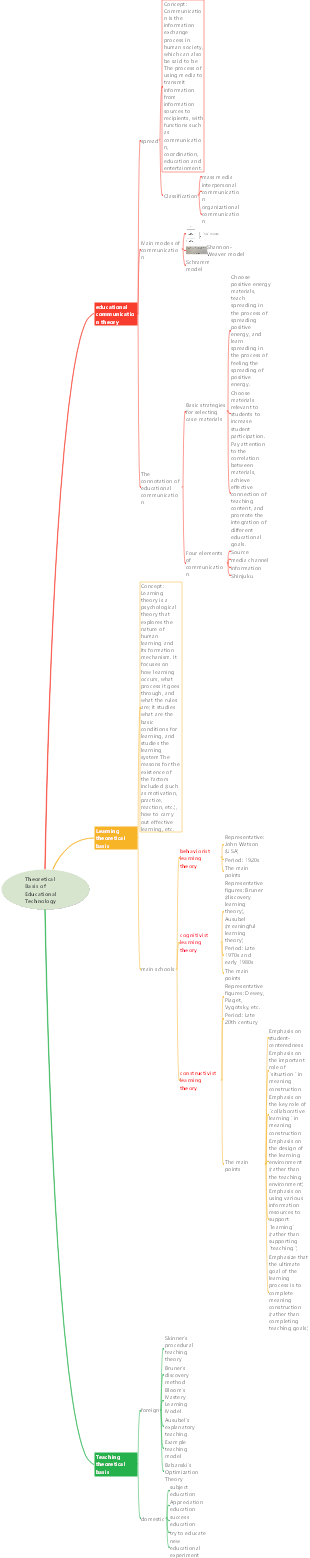
Frontier of Educational Technology Theory—Situated Cognition Theory
Situated cognition theory is a learning theory that emphasizes the situational nature of knowledge and cognition. It believes that knowledge cannot exist abstractly without being separated from specific situations, and learning should be closely integrated with contextualized social practice activities. This theory attempts to correct the shortcomings of traditional learning theories (such as the "stimulus-response" theory of behaviorism and the "information processing" theory of cognitive psychology) in explaining knowledge and cognitive processes, especially their impact on cultural and physical backgrounds. Cognitive neglect.
Edited at 2024-10-15 20:00:01- Il suffit de lire de cette façon Chapitre 5 Création de trois dimensions de la capacité d'apprentissage
Ceci est le chapitre 5 du livre de l'enseignant "This Is Auth to Read", qui parle principalement de ces aspects: ① L'importance de la capacité d'apprentissage ②Comment ajouter un contexte à l'information ③Comment distinguer les connaissances et les informations Je ne vous précipite pas pour remettre en question et défier ⑤Comment utiliser des notes collantes pour mettre à niveau votre capacité d'apprentissage ⑥Pour pourquoi chasser les "biens secs" un pseudo-apprentissage?
- Collection de guide de l'utilisateur Deepseek
Afin d'aider tout le monde à utiliser Deepseek plus efficacement, une collection de Mind Map Deepseek Guide a été spécialement compilée! Cette carte mentale résume le contenu principal: liens liés à Yitu, analyse de profil DS, comparaison des routes technologiques Deepseek et ChatGpt, Guide de déploiement du modèle Deepseek et Qwen, comment gagner plus d'argent avec Deepseek, comment jouer Deepseek, Deepseek Scientific Research Applications Mows Inside Attendez, vous permettant de saisir rapidement l'essence de l'interaction AI. Qu'il s'agisse de la création de contenu, de la planification du plan, de la génération de code ou de l'amélioration de l'apprentissage, Deepseek peut vous aider à atteindre deux fois le résultat avec la moitié de l'effort!
- Instructions d'alimentation Deepseek 30
Il s'agit d'une carte mentale sur les 30 instructions de niveau d'alimentation de Deepseek.
Frontier of Educational Technology Theory—Situated Cognition Theory
- Il suffit de lire de cette façon Chapitre 5 Création de trois dimensions de la capacité d'apprentissage
Ceci est le chapitre 5 du livre de l'enseignant "This Is Auth to Read", qui parle principalement de ces aspects: ① L'importance de la capacité d'apprentissage ②Comment ajouter un contexte à l'information ③Comment distinguer les connaissances et les informations Je ne vous précipite pas pour remettre en question et défier ⑤Comment utiliser des notes collantes pour mettre à niveau votre capacité d'apprentissage ⑥Pour pourquoi chasser les "biens secs" un pseudo-apprentissage?
- Collection de guide de l'utilisateur Deepseek
Afin d'aider tout le monde à utiliser Deepseek plus efficacement, une collection de Mind Map Deepseek Guide a été spécialement compilée! Cette carte mentale résume le contenu principal: liens liés à Yitu, analyse de profil DS, comparaison des routes technologiques Deepseek et ChatGpt, Guide de déploiement du modèle Deepseek et Qwen, comment gagner plus d'argent avec Deepseek, comment jouer Deepseek, Deepseek Scientific Research Applications Mows Inside Attendez, vous permettant de saisir rapidement l'essence de l'interaction AI. Qu'il s'agisse de la création de contenu, de la planification du plan, de la génération de code ou de l'amélioration de l'apprentissage, Deepseek peut vous aider à atteindre deux fois le résultat avec la moitié de l'effort!
- Instructions d'alimentation Deepseek 30
Il s'agit d'une carte mentale sur les 30 instructions de niveau d'alimentation de Deepseek.
- Recommended to you
- Outline
Frontier of Educational Technology Theory—Situated Cognition Theory
Theoretical overview
Situated cognition theory is a learning theory that emphasizes the situational nature of knowledge and cognition. It believes that knowledge cannot exist abstractly without being separated from specific situations, and learning should be closely integrated with contextualized social practice activities. This theory attempts to correct the shortcomings of traditional learning theories (such as the "stimulus-response" theory of behaviorism and the "information processing" theory of cognitive psychology) in explaining knowledge and cognitive processes, especially their impact on cultural and physical backgrounds. Cognitive neglect.
core ideas
01 Concept of knowledge
The development of knowledge and abilities results from ongoing utilization activities in real-life situations
Only by using knowledge in real social situations can we truly understand its connotation and use knowledge correctly and flexibly.
02 Concept of learning
All thinking, learning and cognition are in a specific contextual context, and there is no non-contextualized learning.
Authentic activities are an important way for learners to engage in meaningful and purposeful learning and should become the center of learning
03 Teaching concept
Meaningful learning is only possible when learning is embedded in social and natural contexts in which that knowledge is used
04 Evaluation concept
Assessment must simulate authentic tasks and trigger learners to engage in more complex and challenging thinking
When determining evaluation criteria, it must be taken into consideration that the problem has multiple perspectives and therefore the answer is not unique.
Application of theory in teaching
Stimulate students' positive learning emotions through situations
Promote students’ logical structure through situations
Use situations to drive students to solve real problems
Theoretical Challenges and Prospective Developments
prospect
More possibilities
With the development of the Internet and information technology, the application of educational technology will provide more possibilities for the implementation of situational teaching.
natural health concept
More realistic and immersive
personalization
Situated teaching will increasingly focus on the individual differences and needs of learners. Based on factors such as learners’ interests, learning styles, and learning goals, personalized situational teaching will become an important development direction.
Further integration into education and innovation
The implementation of situational teaching can promote the transformation of education models, cultivate students' innovative thinking and ability to solve practical problems, and promote the all-round development of learners.
challenge
Difficulty of implementation
Creating authentic learning environments can require significant resources and time, which may be difficult to achieve in some cases
Limited scope of application
Certain subjects or learning content may not be suitable for use in real-world settings, which limits the scope of application of the theory
Difficulty
Scenario-based assessments can be more complex than traditional paper-and-pencil tests and require more resources and time to implement.
Characteristics of teaching situations
life
imageability
problematic
Disciplinarity
Emotional
Main content
Emphasize that context is a necessary condition for learning to occur and proceed, and context has clues to guide it function to help retain learning knowledge.
Emphasize that learning must occur in real events
Emphasize that learners must actively engage in practical activities related to the professional field
Learners must be given the right to explore, that is, to gain the right and behavior to be exposed to real dilemmas. Empower the right to find solutions to real dilemmas
origin
In 1987, Reznik of the United States delivered a speech on "Learning in and Out of School." She believed that learning in school is individualized and abstract, while learning outside school has characteristics and advantages such as cooperation, contextualization, and concreteness. This has a milestone role in the development of situated cognition and learning theory.
In 1989, Brown, Collins and Duguid published "Situated Cognition and Learning Culture", arguing that knowledge, thinking and Situation is closely related, knowledge is in the situation and is progressed and developed in behavior.
In March 1993, the authoritative American magazine "Educational Technology" opened a column to discuss situational cognition and learning progress.
Frontier of Educational Technology Theory—Situated Cognition Theory
Theoretical overview
Situated cognition theory is a learning theory that emphasizes the situational nature of knowledge and cognition. It believes that knowledge cannot exist abstractly without being separated from specific situations, and learning should be closely integrated with contextualized social practice activities. This theory attempts to correct the shortcomings of traditional learning theories (such as the "stimulus-response" theory of behaviorism and the "information processing" theory of cognitive psychology) in explaining knowledge and cognitive processes, especially their impact on cultural and physical backgrounds. Cognitive neglect.
core ideas
01 Concept of knowledge
The development of knowledge and abilities results from ongoing utilization activities in real-life situations
Only by using knowledge in real social situations can we truly understand its connotation and use knowledge correctly and flexibly.
02 Concept of learning
All thinking, learning and cognition are in a specific contextual context, and there is no non-contextualized learning.
Authentic activities are an important way for learners to engage in meaningful and purposeful learning and should become the center of learning
03 teaching concept
Meaningful learning is only possible when learning is embedded in social and natural contexts in which that knowledge is used
04 Evaluation concept
Assessment must simulate authentic tasks and trigger learners to engage in more complex and challenging thinking
When determining evaluation criteria, it must be taken into consideration that the problem has multiple perspectives and therefore the answer is not unique.
Application of theory in teaching
Stimulate students' positive learning emotions through situations
Promote students’ logical structure through situations
Use situations to drive students to solve real problems
Theoretical Challenges and Prospective Developments
prospect
More possibilities
With the development of the Internet and information technology, the application of educational technology will provide more possibilities for the implementation of situational teaching.
natural health concept
More realistic and immersive
personalization
Situated teaching will increasingly focus on the individual differences and needs of learners. Based on factors such as learners’ interests, learning styles, and learning goals, personalized situational teaching will become an important development direction.
Further integration into education and innovation
The implementation of situational teaching can promote the transformation of education models, cultivate students' innovative thinking and ability to solve practical problems, and promote the all-round development of learners.
challenge
Difficulty of implementation
Creating authentic learning environments can require significant resources and time, which may be difficult to achieve in some cases
Limited scope of application
Certain subjects or learning content may not be suitable for use in real-world settings, which limits the scope of application of the theory
Assessment difficulty
Scenario-based assessments can be more complex than traditional paper-and-pencil tests and require more resources and time to implement.
Characteristics of teaching situations
life
imageability
problematic
Disciplinarity
Emotional
Main content
Emphasize that context is a necessary condition for learning to occur and proceed, and context has clues to guide it function to help retain learning knowledge.
Emphasize that learning must occur in real events
Emphasize that learners must actively engage in practical activities related to the professional field
Learners must be given the right to explore, that is, to gain the right and behavior to be exposed to real dilemmas. Empower the right to find solutions to real dilemmas
origin
In 1987, Reznik of the United States delivered a speech on "Learning in and Out of School." She believed that learning in school is individualized and abstract, while learning outside school has characteristics and advantages such as cooperation, contextualization, and concreteness. This has a milestone role in the development of situated cognition and learning theory.
In 1989, Brown, Collins and Duguid published "Situated Cognition and Learning Culture", arguing that knowledge, thinking and Situation is closely related, knowledge is in the situation and is progressed and developed in behavior.
In March 1993, the authoritative American magazine "Educational Technology" opened a column to discuss situational cognition and learning progress.