MindMap Gallery PMP-09 Project Resource Management
- 22
- 1
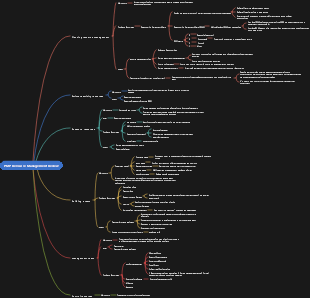
PMP-09 Project Resource Management
Chapter 9 Project Resource Management, PMP project management, PMBOK sixth edition knowledge structure organization, (PMBOK 6th Edition) Essential for studying and preparing for exams, 49 process tests, The ten knowledge areas of PMP, the input and output of the five process groups, PMP Exam—Knowledge Points Review (PMBOK Sixth Edition).
Edited at 2019-08-26 09:18:01- bacteria
This is a mind map about bacteria, and its main contents include: overview, morphology, types, structure, reproduction, distribution, application, and expansion. The summary is comprehensive and meticulous, suitable as review materials.
- Plant asexual reproduction
This is a mind map about plant asexual reproduction, and its main contents include: concept, spore reproduction, vegetative reproduction, tissue culture, and buds. The summary is comprehensive and meticulous, suitable as review materials.
- Reproductive development of animals
This is a mind map about the reproductive development of animals, and its main contents include: insects, frogs, birds, sexual reproduction, and asexual reproduction. The summary is comprehensive and meticulous, suitable as review materials.
PMP-09 Project Resource Management
- bacteria
This is a mind map about bacteria, and its main contents include: overview, morphology, types, structure, reproduction, distribution, application, and expansion. The summary is comprehensive and meticulous, suitable as review materials.
- Plant asexual reproduction
This is a mind map about plant asexual reproduction, and its main contents include: concept, spore reproduction, vegetative reproduction, tissue culture, and buds. The summary is comprehensive and meticulous, suitable as review materials.
- Reproductive development of animals
This is a mind map about the reproductive development of animals, and its main contents include: insects, frogs, birds, sexual reproduction, and asexual reproduction. The summary is comprehensive and meticulous, suitable as review materials.
- Recommended to you
- Outline
09 items Resource management
9.1 Planning resource management
Purpose: Define how to estimate, acquire, manage and utilize resources
During the planning stage, pay attention to the acquisition of scarce resources.
output
resource management plan
Roles and Responsibilities, Training, Team Building, Recognition and Rewards
Project organization chart
Graphically represent project team members and their reporting relationships
Project team resource management
Guidance on defining, staffing, managing, and ultimately demobilizing project team resources
Resource control
Ensure physical resources are available and optimize resource procurement for project needs
Guide how to classify, allocate, manage, and release project resources
Team charter
It needs to be formulated as early as possible and all employees should participate in the formulation.
Tools & Techniques
Data performance
people
(tree) organizational breakdown structure hierarchical
Organizational structure for centralized acquisition of human resources into functional departments
(Table) Responsibility Allocation Matrix RACI
In each task, only one person is A
text type
thing
resource breakdown structure
Authorize
Delegate tasks that you can do faster and better to your team members. If you are unwilling to give up your work, you will never make this transition and may even fall back into the role of a project participant.
Integration work cannot be delegated and one's final responsibility cannot be relieved.
9.2 Estimate activity resources
Estimate the quantity and level of manpower and materials required to execute the project
output
Resource requirements
Identify the types and quantities of resources required for each work package, which can be aggregated to estimate the resources required for each work package, each WBS branch, and for the entire project
Estimate basis
The amount and type of supporting information required for resource estimation varies by application area
resource breakdown structure
Resources are displayed hierarchically by category and type
Project Document Updates Activity Properties Assumption Log Lessons Learned Register
Tools & Techniques
Bottom-up estimation
analogy estimation
parameter estimation
data analysis
Alternatives Analysis
9.3 Access to resources
Obtain the manpower and materials needed for the project
Internal resources are acquired (allocated) by functional managers or resource managers, External resources are obtained through the procurement process
enter
project files
Resource Calendar
output
Project team dispatches work orders
Content: name, role, responsibilities
physical resource allocation order
Content: physical objects, location information
Resource Calendar
The resource calendar identifies the working days and days off when each specific resource is available
Tools & Techniques
pre-dispatch
The person named in the project charter
The person promised in the bid document
Particularly scarce specific people
decision making
Multi-criteria decision analysis
Availability, cost, capabilities, experience, knowledge, skills, attitudes, international factors
Interpersonal and team skills
negotiation
Borrow Mr. Li from the functional manager; grab Mr. Li from the project manager; ask for Mr. Li from external resources.
Negotiation strategy
Deadline, limited power, delay, fair and reasonable, fait accompli, red face or white face
virtual team
A group of people who have little or no time to work face-to-face while completing their work
It is necessary to carry out temporary centralized offices
team role theory
Coordinator, condenser, diplomat, wise man, reviewer, professional, promoter, executor, completer
Project team characteristics
Temporality: Dissolution Anxiety, Loyalty
Goal: Cooperation is to achieve goals
Openness: Boundary openness, changes in team members at different stages
Diversity: Differences in team language, culture and personality
9.4 Building a team
The process of improving work capabilities, promoting interaction among team members, and improving the overall team atmosphere to improve project performance
enter
project files
Resource calendar, project team dispatch work order: carry out different team building for members in different positions
Team charter: a high-level document that guides team building
tool
Centralized office, tight matrix
virtual team
communication technology
interpersonal relationships and team skills
Tuckerman Team five stages of development
Formative stage
Start to know each other, start to understand the project, and become independent of each other
shock stage
During the running-in period, they compete and quarrel with each other.
Standardization stage
Start working together, start trusting each other
mature stage
Solve problems smoothly and efficiently as a unit
dissolution stage
The team completes all the work and the team member leaves the project
excitation
Maslow hierarchy of needs theory
It refers to pursuing the satisfaction of higher-level needs after lower-level needs are satisfied.
Physiological needs (minimum)
Food, clothing, housing and transportation
Safety requirements
Stable and safe
Social needs
Have love, belonging, friends
Respect needs
achieve, be respected, attract attention
Self-actualization needs (highest)
learn, develop
Herzberg two-factor theory
Motivating factors
Corresponding to physiological needs and safety needs
Responsibility, self-actualization, career development, recognition
health factors
Corresponding to respect needs and self-development needs
Working conditions, wages, collegiality, safety, position
McGregor xy theory
Theory X
People are negative and lack enterprising spirit. Adopt command obedience, punishment, and elimination measures
Theory Y
It is assumed that human nature is good, that people are positive and willing to make progress. Use incentives
halo effect
If a person performs well in one aspect, people will think that he is also good in other aspects.
Froome expectancy theory
The fruits of work are very attractive to him and he is motivated to work hard.
Just draw a pie
McClelland achievement motivation theory
Emphasis on differentiating incentives based on the sources of achievement that individuals value more
power, money, sense of achievement
Recognition and Rewards
Only rewards that meet an important need of the recipient are effective rewards.
Senior talent incentives
training
Training costs are to be included in the project budget or borne by the performing organization
Individual and team assessment
Understand members’ strengths and weaknesses, preferences and desires
Available tools are: attitude surveys, ad hoc assessments, structured interviews, competency tests and focus groups
Meeting
Meeting types: project briefings, team building meetings, and team development meetings
output
Team performance evaluation
Evaluation index
Improvement of personal skills
Competency Improvement
Reduction in team member turnover rate
Enhanced team cohesion
9.5 management team (Executive Process Group)
The process of tracking team member performance, providing feedback, resolving issues, and managing team changes to optimize project performance
enter
project files
Problem log
Document who is responsible for resolving specific issues within target dates and monitor resolution
job performance report
Information in performance reports and related forecast reports helps determine future team resource needs, recognition and rewards
Team performance evaluation
Continuous formal or informal evaluation of project team performance helps adjust communication styles, resolve conflicts and improve team interactions
output
change request
tool
interpersonal relationships and team skills
conflict management
Conflict is inevitable and arises from resource scarcity, prioritization, and personal style differences.
Solution
retreat avoidance
Exit (lose-lose)
Moderate and inclusive
Seeking common ground while reserving differences, temporary solution
Compromise and Mediation
Everyone takes a step back (lose-lose)
forced order
The situation is urgent and the conflict is temporarily resolved (win-lose)
Collaborative solution
Sit down and negotiate a solution (win-win)
Make decisions
Influence
related to position
Formal power, reward power, punishment power,
related to human body
expert power, referent power, charismatic power
leadership
Ability to determine and communicate goals and lead subordinates to work towards goals
If you can brag, someone is willing to follow you
Peter's Law
Every position tends to be occupied by an employee who is unable to shoulder his or her responsibilities
Emotional intelligence
Ability to identify and manage emotions in individuals and teams
project management information system
Pay attention to whether team members are willing and able to get the job done
Do you want to & can you?
9.6 Control resources
The process of monitoring actual resource usage and taking necessary corrective actions
enter
job performance data
Contains data about project status, such as the amount and type of resources used
Tools & Techniques
Interpersonal and team skills
Also called "soft skills", they are personal abilities
negotiation
Conduct research on adding physical resources, changing physical resources, or resource-related costs Negotiate
Influence
Influence helps resolve issues promptly and obtain needed resources
8.2 Problem solving
project management information system
data analysis
Alternatives analysis, cost-benefit analysis, performance review, trend analysis
output
change request
job performance information