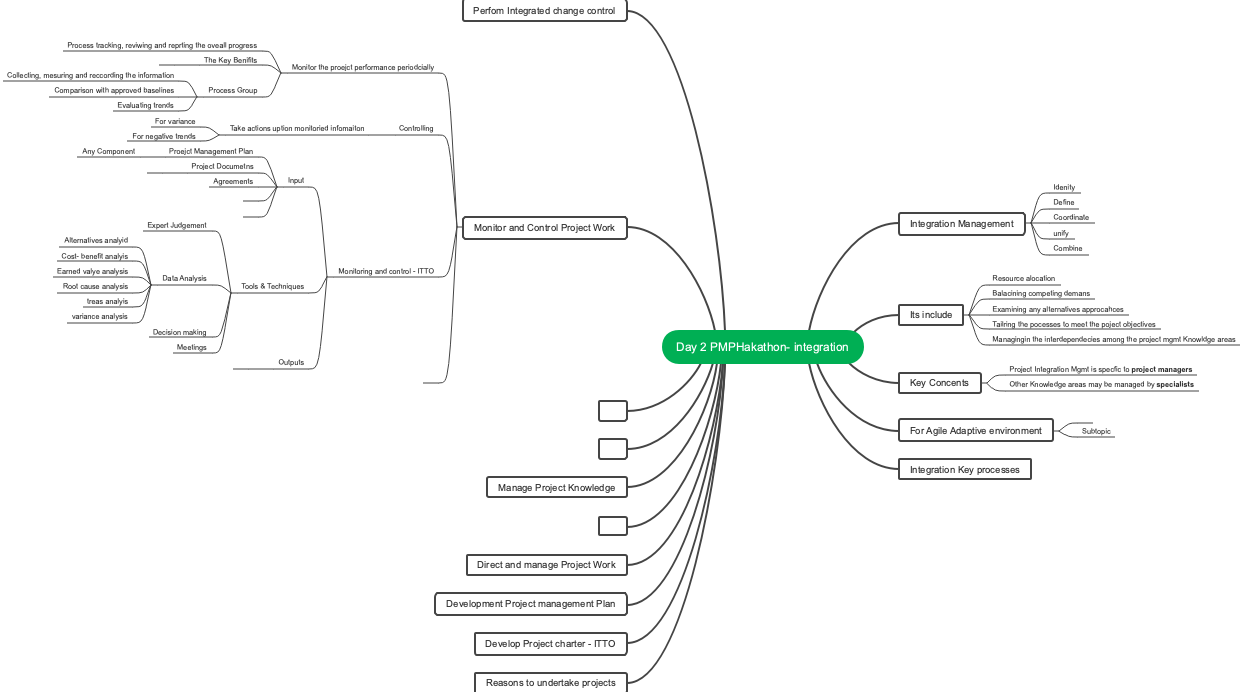
MindMap Gallery PMP General Outline
- 178
- 7
PMP General Outline
PMP general outline,PMP project management, PMBOK sixth edition knowledge structure organization,(PMBOK 6th Edition) Essential for studying and preparing for exams,The ten knowledge areas of PMP, the input and output of the five process groups,PMP Exam—Knowledge Points Review (PMBOK Sixth Edition).
Edited at 2024-09-05 10:02:42- Pathophysiologie - Herzinsuffizienz
Chronische Herzinsuffizienz ist nicht nur ein Problem der Geschwindigkeit der Herzfrequenz! Es wird durch die Abnahme der Myokardkontraktion und der diastolischen Funktion verursacht, was zu unzureichendem Herzzeitvolumen führt, was wiederum Staus im Lungenzirkulation und Stau der systemischen Zirkulation verursacht. Aus den Ursachen sind die pathophysiologischen Prozesse der Herzinsuffizienz für Kompensationsmechanismen komplex und vielfältig. Durch die Kontrolle von Ödemen, die Reduzierung der Vorder- und Nachlast des Herzens, die Verbesserung der Herzkomfortfunktion und die Verhinderung und Behandlung grundlegender Ursachen können wir auf diese Herausforderung effektiv reagieren. Nur durch das Verständnis der Mechanismen und klinischen Manifestationen von Herzinsuffizienz und Beherrschung der Präventions- und Behandlungsstrategien können wir die Herzgesundheit besser schützen.
- Pathophysiologie - Ischämie - Reperfusionsverletzung
Ischämie-Reperfusionsverletzung ist ein Phänomen, dass sich die Zellfunktion und Stoffwechselstörungen und strukturelle Schäden verschlimmern, nachdem Organe oder Gewebe die Blutversorgung wiederhergestellt werden. Zu den Hauptmechanismen gehören eine erhöhte Erzeugung des freien Radikals, die Kalziumüberladung sowie die Rolle von mikrovaskulären und Leukozyten. Das Herz und das Gehirn sind häufige beschädigte Organe, die sich als Veränderungen des Myokardstoffwechsels und ultrastrukturelle Veränderungen, verringerte Herzfunktion usw. manifestieren usw. umfassen die Entfernung von freien Radikalen, die Verringerung der Kalziumüberlastung, die Verbesserung des Stoffwechsels und die Kontrolle von Reperfusionsbedingungen, z.
- Pathophysiologie-Stress
Stress ist ein unspezifischer Schutzmechanismus, der im Körper unter interner und externer Umweltstimulation auftritt, aber übermäßiger Stress kann zu internen Umweltstörungen und -krankheiten führen. Die Stressreaktion beinhaltet mehrere Systeme wie neuroendokrine, zelluläre und körperliche Flüssigkeiten, und seine Hauptmanifestationen umfassen emotionale Reaktionen, Veränderungen der kognitiven Fähigkeiten und Veränderungen des sozialen Verhaltens. Übermäßige Konzentration von Katecholamin ist einer der Hauptmechanismen des Stresses, die körperliche Erkrankungen wie Herz -Kreislauf -Erkrankungen, Stressgeschwüre und psychische Probleme wie traumatische Belastungsstörungen verursachen können. Das Verständnis des Stadiums und des Aufprallmechanismus von Stress kann dazu beitragen, Stress besser zu bewältigen und die körperliche und psychische Gesundheit aufrechtzuerhalten.
PMP General Outline
- Pathophysiologie - Herzinsuffizienz
Chronische Herzinsuffizienz ist nicht nur ein Problem der Geschwindigkeit der Herzfrequenz! Es wird durch die Abnahme der Myokardkontraktion und der diastolischen Funktion verursacht, was zu unzureichendem Herzzeitvolumen führt, was wiederum Staus im Lungenzirkulation und Stau der systemischen Zirkulation verursacht. Aus den Ursachen sind die pathophysiologischen Prozesse der Herzinsuffizienz für Kompensationsmechanismen komplex und vielfältig. Durch die Kontrolle von Ödemen, die Reduzierung der Vorder- und Nachlast des Herzens, die Verbesserung der Herzkomfortfunktion und die Verhinderung und Behandlung grundlegender Ursachen können wir auf diese Herausforderung effektiv reagieren. Nur durch das Verständnis der Mechanismen und klinischen Manifestationen von Herzinsuffizienz und Beherrschung der Präventions- und Behandlungsstrategien können wir die Herzgesundheit besser schützen.
- Pathophysiologie - Ischämie - Reperfusionsverletzung
Ischämie-Reperfusionsverletzung ist ein Phänomen, dass sich die Zellfunktion und Stoffwechselstörungen und strukturelle Schäden verschlimmern, nachdem Organe oder Gewebe die Blutversorgung wiederhergestellt werden. Zu den Hauptmechanismen gehören eine erhöhte Erzeugung des freien Radikals, die Kalziumüberladung sowie die Rolle von mikrovaskulären und Leukozyten. Das Herz und das Gehirn sind häufige beschädigte Organe, die sich als Veränderungen des Myokardstoffwechsels und ultrastrukturelle Veränderungen, verringerte Herzfunktion usw. manifestieren usw. umfassen die Entfernung von freien Radikalen, die Verringerung der Kalziumüberlastung, die Verbesserung des Stoffwechsels und die Kontrolle von Reperfusionsbedingungen, z.
- Pathophysiologie-Stress
Stress ist ein unspezifischer Schutzmechanismus, der im Körper unter interner und externer Umweltstimulation auftritt, aber übermäßiger Stress kann zu internen Umweltstörungen und -krankheiten führen. Die Stressreaktion beinhaltet mehrere Systeme wie neuroendokrine, zelluläre und körperliche Flüssigkeiten, und seine Hauptmanifestationen umfassen emotionale Reaktionen, Veränderungen der kognitiven Fähigkeiten und Veränderungen des sozialen Verhaltens. Übermäßige Konzentration von Katecholamin ist einer der Hauptmechanismen des Stresses, die körperliche Erkrankungen wie Herz -Kreislauf -Erkrankungen, Stressgeschwüre und psychische Probleme wie traumatische Belastungsstörungen verursachen können. Das Verständnis des Stadiums und des Aufprallmechanismus von Stress kann dazu beitragen, Stress besser zu bewältigen und die körperliche und psychische Gesundheit aufrechtzuerhalten.
- Recommended to you
- Outline
PMP General Outline
cross talk
How fast and economical
scope, schedule, quality, cost
81 results (content) (documentation)
136 tools
achievement line
Clues to change: 1 Deliverables (Source: Directing and Managing Project Work) 2 Verified deliverables (Source: Control Quality) 3Accepted deliverables (Source: Validation Scope) 4 Final deliverable handover (source: closing project or phase)
work line
Clues of change (lines of work): 1 Job Performance Data (Source: Directing and Managing Project Work) 2 work performance information (source: 6 controls, 3 supervision, 1 confirmation) 3 Work Performance Report (Source: Monitoring Project Work)
change line
Clues of change (lines of work): 1Change Request (Source: Monitoring Process Group) 2Approved Change Requests (Source: Implementing Holistic Change Control) 3 Confirmed Change Requests (Source: Directing and Managing Project Work)
step: 1. Identify changes (any changes should be reported to the project manager first) 2. Formally propose and record the change (the change request is updated to the change log first) 3. Analyze and evaluate changes; (first review the impact in the field and then conduct a comprehensive review) 4. The project manager submits the changes to the Change Control Board (CCB); (changes involving baselines) 5.CCB approves or rejects the change request and updates the change log; a written decision to approve, reject or suspend the change request 6. Update project management plan and project documents 7. Notify the relevant parties of the changes 8. Implement change requests 9. Review whether approved change requests are implemented in place 10. Summarize experiences and lessons learned.
4Implement overall change control, manage team, manage communication, and control risks
quality line
Quality Management Plan Quality Measurement Indicators
Test and Evaluation Documents
Quality control measurement results
Source: Control Quality
quality report
Source: Management Quality
2 charters
Project Charter
Source: Developing a Project Charter
Team charter
Source: Planning Resource Management
3 1 benchmark
Scope baseline, schedule baseline, cost baseline. performance measurement benchmarks
3 registers
Interested Party Register
Source: Identifying interested parties
risk register
Source: Identifying Risks
Lessons Learned Register
Source: Managing Project Knowledge
3 logs
Hypothetical log
Source: Developing a Project Charter
Problem log
Source: Directing and Managing Project Work
Change log
Source: Implementing Holistic Change Control
2 calendars
Project Calendar
resources, procurement
Develop project schedule and output project calendar
Resource Calendar
Source: Estimate activity resources, obtain resources, implement procurement
4 reports
job performance report
Source: Monitoring Project Work
risk report
Source: Identifying Risks
quality report
Source: Management Quality
final report
Source: Ending a project or phase
2 resources
Project team dispatches work orders
Source: Get Source
material resource allocation sheet
Source: Get Source
2 predictions
progress forecast
Source: Controlling Progress
cost forecast
Source: Control Costs
3 1 Estimation (Tools)
Three major estimates
Estimate resources
Resource requirements
Estimated duration
Estimating duration by resources
Estimate cost
The three major estimation processes all have estimation basis outputs.
Develop project charter
business case
statement of work sow
Project work description
Procurement work description
Project Charter
initiator, authorizer
Determine the candidate for the project manager and determine the availability of resources
Hypothetical log
Assumptions
Constraints
Project operating environment
organizational structure type
organic or minimalist
Decision-making power is given to all employees (discussed)
Functional
The production department, sales department, etc. have strict hierarchies.
All part-time
Part-time employees tend to look down on project work
Division type
Establish different business units according to regional business line customer types, etc.
matrix type
weak matrix shape
There is no project management office and no full-time project manager
balanced matrix type
Established a full-time project manager position
strong matrix type
Established a permanent project management office
Part time part time part time
Communication and management are complex
Most conducive to horizontal communication and integration across departments and professional fields
Project type
Implement project management throughout the organization
Consulting firms can adopt this organizational structure
Special for large projects, all full-time
Repeated allocation of resources for each project reduces resource usage efficiency
virtual
Internet remote working
Hybrid
Project Management Office (PMO) Type
PMO plays a huge role and is the core functional department
business environment factors
internal environmental factors of the organization
environment system
organizational governance framework
Project governance and management must not violate the organizational governance framework
organizational structure
Organizational structure determines the relationship between projects and various levels and departments of the organization
project management information system
Personnel management system
work authorization system
communication system
Resources and Environment
infrastructure
physical resources
cultural environment
group Culture
political atmosphere
management practices
external environmental factors of the organization
Macro environment
Social environment, cultural environment, market conditions, laws and regulations, financial factors, procurement restrictions
Industry environment
Industry standards, business databases, academic research materials, productivity indicators, industry PM book
stakeholder environment
Stakeholder expectations, stakeholder culture, risk thresholds
physical environment
Working conditions, climatic conditions, objective constraints
Any factors that cannot be controlled, avoided, or ignored
May have a positive or negative impact on the project
organizational process assets
Policies, processes, procedures, templates, work templates, work guides and shared knowledge base
If you want to actively use it, it is an asset. If you don't want to use it, but you have to abide by it, it is the environment.
Used to help projects succeed
Lessons learned from past projects, workflows, work templates and work data
Ending a project or phase requires updating: project archives, such as project management plans, change management documents, operational support documents, closing documents, lessons learned summaries
The closer the project is to completion, the lower the risk
Before a project is launched, there is a phase of the project life cycle, such as a feasibility study
Types of project life cycles
Predictive life cycle
Suitable for projects with clear needs
Iterative life cycle
Do one function several times
incremental life cycle
Do several functions in batches
adaptive life cycle
Also called agile or change-driven life cycle, it is a combination of iterative and incremental
For projects with volatile and unclear requirements, use a combination of iterative and incremental methods
hybrid life cycle
A mix of predictive and adaptive
Project manager as integrator
Project managers must not delegate integration management to others, but must do it themselves
Project managers need to understand technology and have certain technical abilities, but they do not need to be technical experts. In particular, project managers cannot be purely experts in a single technical field. Otherwise, he is likely to focus too much on the technical area in which he is good at and neglect the management of the project.
As a manager of interdisciplinary projects, the project manager must be an integrator
Project complexity
project management plan
Sub-management plan
4.1 Change Management Plan
Describe how change requests are formally approved and adopted throughout the project
4.1 Configuration Management Plan
Describe how to record and update project-specific information to ensure Maintain the consistency and effectiveness of products, services or results
5.1 Scope Management Plan
Establish how to define, develop, monitor, control and validate project scope
5.1 Demand management plan
Determine how requirements will be analyzed, documented and managed
6.1 Progress management plan
Establish criteria and define activities for preparing, monitoring and controlling project progress
7.1 Cost Management Plan
Determine how to plan, schedule and control costs
8.1 Quality Management Plan
Determine how the organization's quality policies, methods, and standards will be implemented on projects
9.1 Resource Management Plan
Guide how to classify, allocate, manage and release project resources
10.1 Communication Management Plan
Determine how, when and by whom project information will be managed and disseminated
11.1Risk Management Plan
Determine how to organize and implement risk management activities
12.1 Procurement Management Plan
Determine how the project team will obtain goods and services from outside the performing organization
13.2 Stakeholder participation plan
Determine how to engage stakeholders in the project based on their needs, interests and impacts Decision making and execution.
benchmark
Scope Baseline
Approved scope statement, work breakdown structure (WBS) and corresponding WBS dictionary, used as a basis for comparison
progress baseline
Approved schedule model used as a basis for comparison with actual results.
cost basis
Approved project budget allocated by time period for comparison with actual results basis for comparison
Other components
project life cycle
Describe the series of stages a project goes through from start to finish.
development method
Describe the development approach to a product, service, or outcome, such as predictive, iterative, agile, or hybrid models.
management review
Determine the time point when the project manager and relevant stakeholders will review the project progress to assess whether the performance meets the expectations. period, or to determine whether preventive or corrective action is necessary.
project files
scope management
Collect requirements: requirements documents, requirements tracking matrix, Defining Scope: Project Scope Statement
Progress management
Define activities: activity list, activity attributes, milestone list, Arrange activities in order: activity progress network diagram, Estimated activity time: duration estimate, basis for estimate, Develop schedule: project schedule, schedule data, project calendar, schedule forecast
cost management
Estimating activity costs: cost estimates, basis for estimates Control Costs: Cost Forecasting
Quality Control
Planning quality management: quality measurement indicators, Managing quality: testing and evaluation documentation, quality reports, Control quality: Quality control measurement results,
Resource management
Standardizing Resource Management: Team Charter Estimating activity resources: resource requirements, estimation basis, resource breakdown structure, Obtain resources: material resource allocation orders, project personnel dispatch orders, project calendars,
communication management
Management communication: problem log, project communication record
Risk Management
risk register, risk report
Procurement management
Planning and procurement management: procurement work instructions, procurement documents, supplier selection criteria, seller's proposal, agreement
Stakeholder management
Interested Party Register
Integrated management
Assumption log, change log, lessons learned register
The core of project management
Without exceeding the budget, the project can be fully managed and controlled in all aspects such as time, cost, quality, risk, contract, procurement, human resources, etc., and achieve higher operational efficiency.