MindMap Gallery PMBok 6th Edition
- 101
PMBok 6th Edition
Summary of PMP knowledge points (excluding agile) PMBok Sixth Edition, as an authoritative work in the field of project management, has important guiding significance for project managers and project management teams. It provides the basic framework, knowledge system and best practices of project management, helping project managers to better cope with complex and changing project environments and improve the efficiency and quality of project management.
Edited at 2024-11-29 12:42:24- 把時間當作朋友
這是一篇關於把時間當作朋友的心智圖,《把時間當作朋友》是一本關於時間管理和個人成長的實用指南。作者李笑來透過豐富的故事和生動的例子,教導讀者如何克服拖延、提高效率、規劃未來等實用技巧。這本書不僅適合正在為未來奮鬥的年輕人,也適合所有希望更好地管理時間、實現個人成長的人。
- Treat time as a friend
This is a mind map about treating time as a friend. "Treating Time as a Friend" is a practical guide on time management and personal growth. Author Li Xiaolai teaches readers practical skills on how to overcome procrastination, improve efficiency, and plan for the future through rich stories and vivid examples. This book is not only suitable for young people who are struggling for the future, but also for everyone who wants to better manage time and achieve personal growth.
- 高效能人士的七個習慣
這七個習慣相輔相成,共同構成了高效能人士的核心特質。透過培養這些習慣,人們可以提升自己的領導力、溝通能力、團隊協作能力和自我管理能力,從而在工作和生活中取得更大的成功。
PMBok 6th Edition
- 把時間當作朋友
這是一篇關於把時間當作朋友的心智圖,《把時間當作朋友》是一本關於時間管理和個人成長的實用指南。作者李笑來透過豐富的故事和生動的例子,教導讀者如何克服拖延、提高效率、規劃未來等實用技巧。這本書不僅適合正在為未來奮鬥的年輕人,也適合所有希望更好地管理時間、實現個人成長的人。
- Treat time as a friend
This is a mind map about treating time as a friend. "Treating Time as a Friend" is a practical guide on time management and personal growth. Author Li Xiaolai teaches readers practical skills on how to overcome procrastination, improve efficiency, and plan for the future through rich stories and vivid examples. This book is not only suitable for young people who are struggling for the future, but also for everyone who wants to better manage time and achieve personal growth.
- 高效能人士的七個習慣
這七個習慣相輔相成,共同構成了高效能人士的核心特質。透過培養這些習慣,人們可以提升自己的領導力、溝通能力、團隊協作能力和自我管理能力,從而在工作和生活中取得更大的成功。
- Recommended to you
- Outline
PMBok 6th Edition
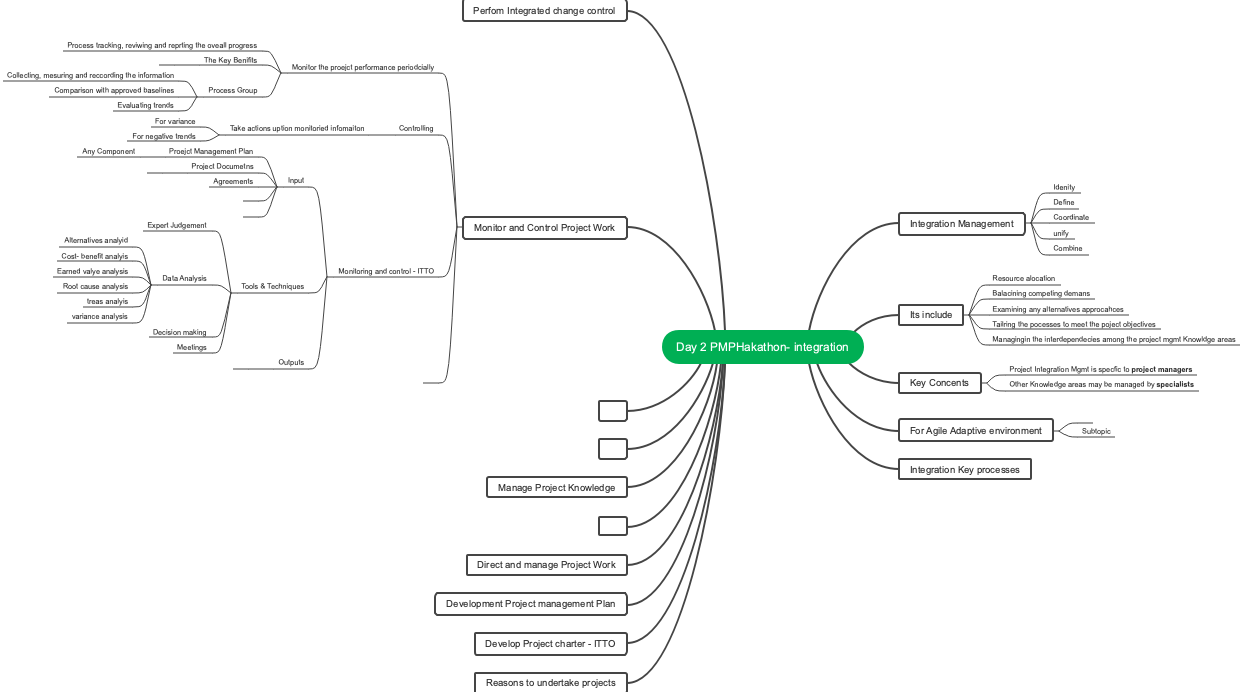
Project integration management
Project Charter
business case
Use this to decide whether the desired results of the project are worth the investment.
The sponsor uses this document as a basis for approval, rejection, and project or phase decisions
The cost and income expectations in this document are based on business environment factors. If business environment factors change Renew the business case
The project manager can perform business justification and must re-do the justification when it is discovered that the business environment factors have changed or are incorrect. and report
expert judgment
Rarely take exams
a judgment estimating tool
If the project manager girl has experience and has never done similar projects: 1. Leverage organizational process assets 2. Turn to subject matter expert SMEs
brainstorming
Get lots of ideas in a short amount of time
focus group
Interactive discussions led by trained moderators
Interview
Chat directly with stakeholders to obtain information
Can be one-to-one or include multiple interviewers or interviewees
Can be used to obtain confidential information
Boot Facilitation
Used to coordinate and unify the different opinions of two or more parties
Three characteristics: Disagreements across departments or multiple parties fast reach consensus
Hypothetical log
Document high-level strategic and operational assumptions and constraints identified during project initiation
The records identified during the startup process are recorded in the hypothesis log, and the records identified during the rest of the process are recorded in the risk register.
Assumptions: factors that the project success depends on and that the project manager cannot control
Constraints: Objective factors that limit the choice of project managers (negative career environment factors)
project management plan
Checklist
It is a list of tasks that need to be performed or checked in case they are missed.
kick-off meeting
Pay attention to the difference between initiating meeting and initiating meeting
Four themes: Present project plan and communicate project goals Assign roles and responsibilities Gain team commitment to the project (roles and responsibilities) Team members get to know each other and establish communication channels
Direct and manage project work
Project Management Information System PMIS
All information technology software tools related to project management used by enterprises, generally not selected
deliverables
Compared with the final product or service results, the deliverables are its components and partial results.
Problem log
Project documentation to record and follow up on all issues
Three elements: what is the problem, who will be responsible for solving it, and when will it be solved?
What has happened is a problem, what is uncertain is a risk
First record the problem log, then analyze, then deal with it, and summarize the experience and lessons after handling it.
Managing project knowledge
At the end of the project or phase, the relevant information is included in the lessons learned knowledge base and becomes part of the organizational process assets.
For the future, for other projects, when starting a new project, refer to the organizational process assets
Monitor project work
Alternatives analysis
Find the best value for money among two or more solutions
cost benefit analysis
Compare benefits and costs to ensure benefits are higher than costs, mostly used to select projects and alternatives
Pay attention to distinguishing between benefit management plans: whether the project is worth doing, what is the goal, and whether the project is successful (it may lose money but is in line with the company's strategy)
Earned value analysis
Quantitatively analyze scope, schedule, and cost performance, and predict future performance
root cause analysis
Identify the root cause of the problem. Can be used for quality defects, process out of control, scope, schedule, cost performance deviations Team performance, morale, stakeholders and other issues
trend analysis
Predict whether future performance will be better or worse
Deviation analysis
Analyze the differences, causes and extent of deviations between actual and planned to determine whether to take measures
Implement holistic change control
1. Throughout the project, the project manager bears the ultimate responsibility 2. At any time throughout the project life cycle, any stakeholder involved in the project can submit a change request 3. The Change Control Board (CCB) is responsible for approving or rejecting changes. 4CCB’s decisions should be recorded (change log) and communicated to relevant parties
Change processing flow (priority) Follow the overall change process or follow the change management plan (one-size-fits-all option) written record impact analysis CCB approval Update change log/update project management plan Implement changes
Changes to the communication management plan, stakeholder management plan, and resource management plan are not considered
End project or phase
If terminated early before completion, the reason for termination must be stated in the formal closing document
final report
The last performance report submitted and presented to stakeholders at the end of the project to summarize the project completion status
Project or phase closure documents
Summarize lessons learned→Update to organizational process assets
The project manager must complete the lessons learned summary before starting a new project
The project manager is responsible and cannot be replaced by others
project scope management
planning scope management
project scope management plan
procedural planning
demand planning
Describe how to analyze, document, and manage project and product requirements
Gather requirements
Emphasis on stakeholder participation and avoid closed doors
Questionnaire
Large audience, wide distribution, fast, and capable of statistical analysis
Benchmarking
Comparison of practices with other comparable organizations, i.e. imitation, reference, copycat
voting decision
Delphi: anonymous voting
Unanimous: everyone agrees
Most Agree: More than 50% agree
Relative majority agreement: decision-making based on the opinions of a relative majority, with more than two options
autocratic decision-making
Don’t choose the exam
Multi-criteria decision analysis
Consider multiple indicators for decision-making, usually using a scoring method, such as Gao Fu Shuai in the blind date market
Affinity diagram
Categorizing ideas generated by brainstorming
mind map
Integrate tools and emphasize connections
nominal group technique
Secret ballot sorting
prototype method
Get early feedback on requirements, i.e. MVP
Requirements Tracking Matrix
Ensure that each requirement has business value and provide a method to track requirements throughout the project life cycle , ensuring that requirements can be delivered at the end of the project
Define scope
project scope statement
Represents the consensus among project stakeholders on the project scope
Test points: If everyone disagrees on the scope later, please check this manual.
Four elements: product scope description, deliverables, acceptance criteria, exclusions
Create WBS
Only traditional project management has Defines the overall scope of the project and represents the work specified in the approved current project scope statement Tools: Decomposition (rolling planning)
Scope Baseline
Three elements: scope statement, WBS, WBS dictionary
work package
The lowest level of WBS work can estimate and manage its cost and duration.
Control account CA
There is a layer in the middle of the WBS where budgets are allocated and costs are controlled.
Requirements Tracking Matrix
Information related to requirements, including how to confirm requirements
Confirm scope
The process of formal acceptance of completed project deliverables by the client or sponsor
span of control
Scope CreepScope Creep
Uncontrolled expansion of product or project scope, with corresponding adjustments to time, cost, and resources
tool
Deviation analysis: 1. Identify the deviation 2. Cause analysis (root cause analysis or cause and effect diagram) 3. Take measures
Acceptance failed
Prediction: Regardless of verification or acceptance, failure → go through the change process
Agile: Update PB, prioritized by PO
Project progress management
Planning progress management
Project schedule management plan
Procedural plan guides all progress management work
Define activities
Break down work packages into schedule activities
tool
break down
rolling planning
output
Activity list
Activity attribute list
Milestone List
Sequence activities
SS: start to start FS: end to beginning FF: end to end SF: start to finish
mandatory dependencies
Typically related to objective constraints, such as equipment or resource availability
selective dependency
Create an order based on best practices
external dependencies
Not within the team's control, such as suppliers, etc.
internal dependencies
under team control
lead time
The amount of time that a successor activity can be advanced relative to its predecessor activity
Hysteresis
The amount of time that the successor activity needs to be delayed relative to its predecessor activity
Project progress network diagram
Graphics that represent logical relationships or dependencies between project schedule activities (milestones can also show dependencies)
Estimate activity duration
Traditional projects: 1. Analogous estimation (refer to historical projects) 2. Parameter estimation (historical projects and statistical models) 3. Bottom-up (WBS) 4. Reserve analysis (contingency and management reserves) 5. Three-point estimate (considering uncertainty and risk) Agile projects: 1. Delphi (Planned Poker) 2. Relative estimation
Resource Calendar
Shows when a specific resource is available during the project and for how long
Whenever you see that a resource is unavailable: update the resource calendar; or schedule tasks → refer to the resource calendar
Develop a progress plan
critical path
The critical path is the longest sequence of activities in a project and determines the shortest possible project duration.
The critical path does not consider resource constraints; the critical path must exist but is not necessarily unique; the total float time is generally 0
total float
The amount of time an activity can be postponed or delayed without affecting the minimum duration of the entire project
Calculation formula: total floating time = latest start - earliest start or latest completion - earliest completion of this activity
free float
The amount of time an activity can be postponed without affecting the earliest start of the successor activity
Calculation formula: earliest start of successor activity - earliest completion of stupid activity
Resource optimization
By adjusting activity start and completion dates, resource constraints can be solved in the following two ways:
resource balancing
Will cause the critical path to become longer
resource smoothing
The project critical path will not be changed and the completion date will not be delayed.
What-if scenario analysis
Based on the existing schedule, consider various schedule risks, evaluate the feasibility of the schedule under different conditions, and prepare schedule reserves and contingency plans to deal with the impact of unexpected situations.
Progress compression
Without reducing the scope of the project, shorten or overtime the progress period to meet schedule constraints, mandatory dates, etc., which are divided into the following two types
rush work
It will definitely increase the cost. If you have abundant resources, you can choose
Add resources to activities on the critical path, such as overtime
Quick follow up
Does not increase costs, but increases risks
Change the original serial to parallel on the critical path
Project schedule
A document containing the planned start and planned finish dates for each activity, as well as the planned start and planned finish dates for the entire project
progress baseline
The approved schedule is called the schedule baseline
bar chart
The horizontal bar represents the duration of the activity from start to finish date
milestone chart
Similar to a bar chart, but only identifies planned start or completion dates for major deliverables and key external interfaces
Resource histogram
Resource requirements calculated by time period, quantity of resource requirements per unit time
Project Calendar
Natural Calendar (365 days a year) > Project Calendar (minus holidays) > Resource Calendar (Available Time of Resources)
When the project is planned to be carried out
control progress
Any change that changes the project start or completion date is called a schedule baseline change and must go through the overall change control process.
project cost management
planning cost management
Project cost management plan
A procedural plan that describes how to plan, schedule, and control project costs
Estimate cost
An estimate of the costs required to complete a single work package or activity is the basis for developing a budget
The accuracy of project estimates will gradually improve as the project progresses
Contingency Reserve: A portion of the budget included in the cost baseline to address known and unknown risks As project information becomes clearer, contingency reserves can be drawn down or reduced The project manager has direct control and is also responsible for the project
Make a budget
management reserve
A budget specifically set aside for management control purposes to address unknown-unknown risks
Management reserves are not included in the cost baseline
When the management reserve is used, the cost baseline needs to be increased, resulting in a change in the cost baseline, which requires a change process.
cost basis
Approved project budget allocated by time period, excluding any management reserves
Control costs
The process of managing cost baseline changes
When the BAC changes, it is called a cost baseline change and must be handled through the overall change control process.
SPI measurement
BAC: Total PV, excluding management reserves
EV: The value of work actually completed by the team so far
PV: The value of the work currently planned to be completed by the team
AC: How much has it actually been spent so far?
Progress performance SPI=EV/PV
Cost performanceCPI=EV/AC
SV=EV-PV
CV=EV-AC
All states >0 and >1 are good, and vice versa. SV and SPI need to be viewed in conjunction with the critical path. If there is no special instructions, the default critical path will be used. If the non-critical path SPI>1, it means that the progress is behind, indicating that a large number of non-critical paths have been completed.
Project quality management
Quality is the degree to which the intrinsic characteristics of a set of things meet needs Levels are expressions that serve the same purpose but have different level parameters. So low quality is definitely a problem, but low grade is not necessarily a problem. Prevention is better than inspection
Plan quality management
quality cost
consistency cost
Ensure results meet required quality costs
prevention cost
Work implemented to prevent results from not meeting requirements, such as training, documentation, equipment maintenance, choosing the right time to do things, etc.
Evaluate costs
Work to check whether deliverables meet quality requirements, such as testing, destructive experiments, inspections, etc.; can reduce external failure costs
non-conformity cost
internal failure costs
The project team discovered
external failure costs
customer discovery
quality management plan
Describe how applicable policies, procedures, and guidelines will be implemented to achieve quality objectives
Test point: Modify or change the quality management plan → follow the change process, common description: reduce the scope and extent of testing, etc.
quality measures
Stakeholders must be involved when defining to prevent failure of acceptance
Management quality
Apply the organization's quality policy to the project, And the process of transforming quality management plans into unexecutable quality activities
process analysis
Continuous improvement and improvement
It is an important tool for quality assurance with the purpose of improving the process and can be considered as part of the quality audit process.
root cause analysis
Determine the root causes of deviations, defects or risks
Eliminating the root cause prevents the problem from recurring
Cause and Effect Diagram (Fishbone Diagram)
Identify the main or root cause of the problem, and deduce the cause based on the results
If the question says to find the cause, choose the cause and effect diagram If the emphasis is on preventing recurrence, select Root Cause Analysis
Histogram
Use a bar chart to display the number and causes of defects for each deliverable.
Pareto chart
Prioritize
Histogram sorted by number of defects from high to low
When asked what to prioritize, choose Pareto chart
Scatter plot
Shows whether there is a relationship between two variables
quality audit
Two goals: 1. Compliance 2. Build confidence in the future
Structured and standardized summary of lessons learned
Focus on quality management processes and policies, rather than the deliverables themselves
X-oriented reference (DFX)
Technical guidance on optimizing specific aspects
problem solving process
Define the problem→Identify the root cause→Generate possible solutions→Select the best solution→Execute the solution→Verify solution effectiveness
Control quality
Keywords: deliverables
examine
Refers to checking deliverables
Cause and effect diagrams, scatter diagrams, and Pareto charts can all be used
Testing/Product Evaluation
Identify errors, defects, vulnerabilities or other non-compliance issues in products or services
control chart
Usage scenarios: 1. Process stability 2. Is it controlled? 3. Batch generated tracking 4. Whether the improvements are effective
Used to determine whether a process is stable and has predictable performance
Two situations of loss of control
One-point rule: There is a measurement point that exceeds the upper or lower control limit
Seven-point rule: If 7 consecutive measurement points are on the same side of the mean line, it is out of control even if the upper and lower limits are not exceeded.
Specification upper and lower limits
Contract or Customer or Sponsor Definition
Control upper and lower limits
The project manager and management team decide
Check whether there are any problems with the control chart After discovering the problem, use the cause and effect diagram to find the cause After the cause is found, use a scatter plot to determine whether the two elements are related. Finally, a Pareto chart is used to determine the order of processing.
Project resource management
Team members are involved in the planning stage, It not only allows them to contribute their professional skills to the project work, but also enhances their sense of responsibility for the project.
Emotional intelligence
Project managers should enhance their personal emotional intelligence by improving their internal (such as self-management and self-awareness) and external (such as relationship management) abilities. Can improve team efficiency and reduce turnover rate
self-organizing team
Typically staffed by generalists rather than subject matter experts who can continually adapt to changing circumstances and incorporate constructive feedback
Virtual Teams/Distributed Teams
Teams working on the same project but in different locations
Different countries, regions, time zones, cultures → virtual teams → preferred communication
Planning resource management
Responsibility Allocation Matrix (RAM/RACI)
Whenever you see multiple people responsible for one thing, first look for the responsibility allocation matrix This is not available in Agile because Agile teams self-organize
Used to show the relationship between work packages or activities and project team members; ensuring that only one person is involved in any task to avoid unclear authority
resource management plan
Insufficient ability: choose training
A guide on how to classify, allocate, manage and release project resources
Project organization chart
Graphically represent project team members and their reporting relationships
Team Charter (Basic Rules)
If team meetings are not efficient, use team charters; Should be developed together by team members
Creates a document for the team about team values, consensus, and work guidelines; establishes clear expectations for acceptable behavior among team members
Estimate activity resources
The process of estimating the type and quantity of team resources, materials, equipment and supplies required to execute a project
Resource requirements
Identify the types and quantities of resources required for each work package or activity within a work package
Resource Breakdown Structure (RBS)
It is a hierarchical display of resource categories and types.
Get resources
internal resources
Obtained from the functional manager or resource manager, the project manager needs to negotiate with the resource manager to obtain it.
external resources
Procurement obtained
How to get it
pre-dispatch
virtual team
Project team dispatches work orders
Building the team
Improve work ability, promote interaction among team members, improve team atmosphere, and improve project performance
Team work is a key factor in project success
Tuckman's ladder theory (5 stages)
form
Clear responsibilities
Storm in the shock stage
Intense conflict, struggle for power
What about the project manager? Find the project charter
Norm stage
Start collaborating and trusting each other
Mature stage Perform
well organized
dissolution stage
Finish the work and leave the project
Centralized office
Co-locate most or all of the most active project team members in the same physical location
virtual team
Leverage remote technology to create an online team environment
Interpersonal and team skills
Conflict management/influence/motivation/negotiation/team building
team building
Whenever you see problems with collaboration or coordination, low morale, or low performance, look for team building
By holding various activities, we strengthen the social relationships of the team and create a positive and cooperative working environment, aiming to help members work together more effectively.
Recognition and Rewards
Cultural differences should be considered when determining recognition and rewards
Customized rewards, taking members’ needs into consideration
Generally, direct monetary rewards are not selected for exams.
Project managers should base recognition as much as possible throughout the project cycle rather than waiting until the project is completed
training
Insufficient ability, looking for training
Management team
Track team members' performance, provide feedback, resolve issues and manage team changes
conflict management
If a disagreement becomes a negative, it should be resolved by a team member If conflict escalates, the project manager should provide assistance to facilitate a satisfactory solution
retreat/evade
Postponing problems until you are more prepared or pushing them to others
Easing/accommodating
Emphasize consistency rather than difference and take a step back to maintain harmony
Compromise/Mediation
Find a solution that satisfies all parties to a certain extent (possibly lose-lose)
force/command
Power is often used to forcefully solve urgent problems
Collaboration/Problem Solving (Best)
If it is judged that there is a critical moment, generally choose force, and the other options are cooperation to solve the problem.
Integrating different concepts and opinions, using a cooperative attitude and open dialogue to guide all parties to reach consensus and commitment, a win-win situation can be achieved
Emotional intelligence
Refers to the ability to identify, assess, and manage personal emotions, the emotions of others, and the emotions of groups
Control resources
Ensure physical resources are allocated to projects as planned and monitor actual resource usage according to resource usage plans
Ensure allocated resources are available to projects in a timely manner and are released when no longer needed
Project communication management
Planning communication management
Communication needs analysis
Analyze communication needs and determine information requirements of project stakeholders
You cannot do things behind closed doors. You must determine the content, method, and frequency of communication based on the specific needs of different stakeholders.
Sensitivity and Confidentiality of Information
When developing a communications management plan, consider the sensitivity and confidentiality of information and develop a social media policy for employees to ensure appropriate behavior, information security and intellectual property protection.
feedback/response
After understanding the received information, the receiver passes the restored thoughts or opinions to the original sender to confirm whether it was understood correctly, which is a guarantee of communication quality.
Sender's Responsibilities
Responsible for the delivery of information, ensuring the clarity and completeness of information, and confirming that information has been correctly understood
Recipient’s Responsibilities
Receive information completely, understand it correctly, and need to be informed that it has been received or respond appropriately
communication method
interactive communication
Important communicators or important stakeholders
Also called interactive communication, real-time multi-directional information exchange between two or more parties, such as meetings, telephone and video conferences
push communication
Send or publish information to specific recipients who need to receive the information, such as text messages, emails, etc.
Can ensure delivery, but does not ensure the message is delivered or understood by the target
pull communication
Suitable for large amounts of complex information or large information audiences, such as portals, experience and lesson libraries, etc.
communications management plan
Describe how to plan, structure, execute and monitor project communications to improve communication effectiveness
Not receiving, receiving too much, not being able to understand, or having new management requirements = dissatisfaction with communication
Whenever someone is dissatisfied with communication → look for a communication management plan
management communication
Conference management
Prepare agenda, invite important attendees and ensure their attendance; handle on-site conflicts
active listening
Includes notification of receipt, clarification and confirmation of information, understanding, and elimination of glitches that prevent understanding
job performance report
Typical examples: status reports and progress reports
Includes: Earned Value Charts, Trendline Forecasts, Reserve Burndown Charts, Defect Histograms, Contract Performance Information, and Risk Overview Analysis
Project communication record
Project communication artifacts include, but are not limited to: performance reports, deliverable status, schedule progress, costs incurred, demonstrations, and other information required by stakeholders
Supervise communication
Ensure that the communication needs of the project and its stakeholders are met, and the process of optimizing the information transfer process according to the requirements of the communication management plan and stakeholder participation plan
project risk management
Risk is uncertainty The goal of risk management is to control uncertainty in some way so that risk exposure is controllable Three elements: risk events, probability, and impact
risk threshold
It reflects the risk preference of the organization and project stakeholders, and is the acceptable degree of variation in project goals.
planning risk management
risk management plan
Describe how to organize and implement risk management activities
Procedural plan, cannot be changed directly
risk category
Risk categories are usually constructed with the help of a risk breakdown structure (RBS). The risk breakdown structure is a hierarchical presentation of potential risk sources and is very useful for identifying risks or classifying identified risks.
Probability and Impact Matrix
Risk ranking rules, listing both opportunities and threats
Risk value = probability * impact
Identify risks
Main tools
Expert judgment, brainstorming, checklists, interviews, root cause analysis, assumptions and constraints analysis, SWOT analysis
SWOT analysis
According to the organization's own strengths and weaknesses (S, W), and the opportunities and threats of the external environment (O, T)
risk register
Record details of identified individual project risks; list of identified risks/persons responsible for potential risks/list of potential risk response measures
risk report
non-disposable
Qualitative risk analysis
Tool: Probabilistic Impact Assessment/Matrix
Identify responsible persons for each risk
Risk classification
Categorizing risks helps focus attention and managers on areas with the greatest risk exposure
Low priority risk watch list
After qualitative analysis, important risks with high priority enter the quantitative risk analysis process and planning risk response process for further processing. Low-priority records are monitored in this list.
Quantitative risk analysis
simulation
Use models to simulate the effects of individual risks and other uncertainties, often using Monte Carlo simulations
sensitivity analysis
Ask which risk has the greatest impact on the project → sensitivity analysis
Decision tree analysis
Use the comprehensive average result to select the best solution from several alternatives
Plan risk responses
Threat response strategy
Report
Beyond the authority of the project manager, such as changes in laws and regulations
avoid
100% avoidance (note the inference of innocence)
transfer
Transfer to third party, outsourcing, insurance, etc.
alleviate
Reduce the probability and impact of risks, such as redundancy, more reliable sellers
accept
Accepts that threats exist but does not proactively take measures, such as establishing contingency reserves, reserving resources or conducting periodic reviews, etc.
Opportunity coping strategies
Report
open up
Allocate the most capable resources, or adopt new technologies or technology upgrades to save costs and shorten time
share
improve
Raise the probability and impact, such as increasing resources to seize the market as soon as possible
Increasing resources is improving The most powerful resource to increase is to develop
accept
emergency response strategies
Only take corresponding measures when specific events occur
Overall project risk response strategy
avoid/exploit/mitigate or enhance/accept
FALL back plan
Spare tire; used when risks occur and primary countermeasures are insufficient
secondary risk
Risks directly caused by the implementation of countermeasures
residual risk
There are still risks after taking measures, such as if a person carrying an umbrella does not get wet and his shoes get wet
Implement risk responses
Execute agreed responses as planned to manage overall risk exposure
Oversight risk
Reserve analysis
Refers to the project comparing the remaining contingency reserve with the amount of remaining risk at any point in time to determine whether the remaining reserve is still reasonable
risk audit
Assess risk management process effectiveness
risk review meeting
Identify new risks; reassess current risks; close obsolete risks
Project Procurement Management
Includes the various processes involved in procuring or obtaining required products, services, or results from outside the project team
Planning Procurement Management
Is the process of recording project procurement decisions, clarifying procurement methods, and identifying potential sellers
Contract type
Total price category
Use when requirements are clearly defined and no major scope changes will occur
Fixed Total Price FFP
The most commonly used contract type, the most friendly to Party A, and the risk lies with Party B; the price is fixed from the beginning and is not allowed to change unless the scope of work changes.
Total price plus incentive fee FPIF
Allow certain performance deviations and provide financial rewards for achieving targets; this contract will set a price ceiling, and all costs above the upper line will be borne by the seller
Total price plus economic price adjustment
Two situations apply: 1. The seller’s performance period will span several years; 2. The price will be paid in different currencies.
cost compensation
The scope of work is expected to undergo major changes during the execution of the contract, which is friendly to Party B
Cost plus fixed fee CPFF
Party A reimburses Party B for all deductible costs incurred in performing the contract work and pays a fixed fee to the seller
Cost Plus Incentive Fee CPIF
Party A reimburses Party B for all deductible costs incurred in performing the contract work, and pays a predetermined incentive fee when the seller reaches the performance targets stipulated in the contract.
cost plus incentive fee
The keyword is subjective performance standard, generally not selected
Reimburse the seller for all legitimate costs, but pay most of the costs to the seller only if the seller meets certain subjective performance standards stipulated in the contract
mixed type
Work and materials contract T&M
Fixed unit price, suitable for situations where accurate work instructions cannot be compiled quickly; such as expanding staff, hiring experts, or seeking external support
Self-purchase or outsourcing analysis
Procurement Management Plan
Bidding documents
Information invitation
Invitation for quotation
Invitation for Proposal
Procurement Statement of Work SOW
Implement procurement
bidders meeting
Procurement negotiation
Contract (agreement)
Control purchasing
Claims management
Procurement audit
Procurement closed
Procurement file
Project stakeholder management
1. Identify all, manage key points, and participate as early as possible 2. As long as the stakeholder is not satisfied, the first choice is to communicate to understand the needs and questions. If you want to communicate, you need to have a meeting and talk to him.
Identify stakeholders
mind writing
Improved form of brainstorming, not often tested
Stakeholder analysis
Stakeholder analysis produces a list of stakeholders and various information about them
rights interest grid
four quadrants 1. Great power, high benefits - focus on management 2. Great power, low benefits - satisfy them 3. Little power, low benefits - supervision 4. Little power, only interests - inform at any time
highlight model
Can be used to determine the relative importance of identified stakeholders
Stakeholder classification tool, suitable for large communities of complex stakeholders or complex relationship networks within the community of stakeholders.
Stakeholder register
Whenever there is a change in a stakeholder, the stakeholder register is updated first.
The main output is used to record the information of identified stakeholders, including but not limited to identity information and assessment information.
Planning stakeholder engagement
Stakeholder participation level classification
Don't understand type
Resistant
Neutral
Supportive
Understand the project and its potential impacts, and will support the project work and its outcomes
leadership type
Stakeholder Engagement Plan
Strategies and actions to promote effective stakeholder participation in decision-making and execution
Manage stakeholder engagement
Communicate and collaborate with stakeholders to meet their needs and expectations and facilitate the process of appropriate stakeholder participation; Main function: Allow project managers to increase stakeholder support and reduce resistance As long as the stakeholder is not satisfied, talk to him or her and understand the demands through communication.
communication skills
When carrying out the management stakeholder participation process, adopt corresponding communication methods for each stakeholder according to the communication management plan
Interpersonal and team skills
Conflict Management/Cultural Awareness/Negotiation/Observation and Conversation/Political Awareness
Oversee stakeholder engagement
Supervise project stakeholder relationships and guide stakeholders to reasonably participate in the project by revising participation strategies and plans
agile