MindMap Gallery respiratory system
- 59
respiratory system
Regarding the mind map of the respiratory system, the respiratory tract includes the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea and bronchi, etc., and is responsible for transporting gases. The lungs include lung parenchyma and interstitium, which are the sites of gas exchange.
Edited at 2024-01-14 21:27:08- bacteria
This is a mind map about bacteria, and its main contents include: overview, morphology, types, structure, reproduction, distribution, application, and expansion. The summary is comprehensive and meticulous, suitable as review materials.
- Plant asexual reproduction
This is a mind map about plant asexual reproduction, and its main contents include: concept, spore reproduction, vegetative reproduction, tissue culture, and buds. The summary is comprehensive and meticulous, suitable as review materials.
- Reproductive development of animals
This is a mind map about the reproductive development of animals, and its main contents include: insects, frogs, birds, sexual reproduction, and asexual reproduction. The summary is comprehensive and meticulous, suitable as review materials.
respiratory system
- bacteria
This is a mind map about bacteria, and its main contents include: overview, morphology, types, structure, reproduction, distribution, application, and expansion. The summary is comprehensive and meticulous, suitable as review materials.
- Plant asexual reproduction
This is a mind map about plant asexual reproduction, and its main contents include: concept, spore reproduction, vegetative reproduction, tissue culture, and buds. The summary is comprehensive and meticulous, suitable as review materials.
- Reproductive development of animals
This is a mind map about the reproductive development of animals, and its main contents include: insects, frogs, birds, sexual reproduction, and asexual reproduction. The summary is comprehensive and meticulous, suitable as review materials.
- Recommended to you
- Outline
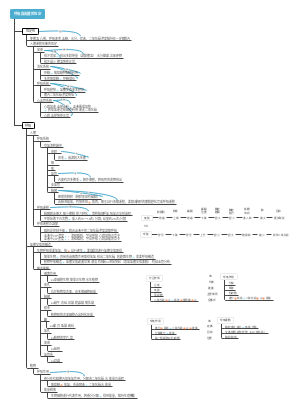
respiratory system
nose
Summary
It is both the beginning of the respiratory tract and the organ of smell
Divided into external nose, nasal cavity, paranasal sinuses
external nose
Root of nose, dorsum of nose, tip of nose, wing of nose
nasal cavity
Divided by nasal threshold
Anterior part: nasal vestibule
Posterior part: proper nasal cavity
several concepts
nasal threshold
Arc-shaped bulge above nasal vestibule
nasal septum
A scaffold composed of the vertical plate of the ethmoid bone, vomer bone, and septal cartilage
paranasal sinuses
General term for the air bones surrounding the nasal cavity
Frontal sinus, ethmoid sinus, sphenoid sinus, maxillary sinus
throat
Summary
respiratory tract, vocal organ
The upper boundary is the epiglottis cartilage, and the lower boundary is the lower edge of the cricoid cartilage. Mainly composed of laryngeal cartilage and laryngeal muscles
The upper part leads to the pharynx, the lower airway, the infrahyoid muscles in front, the hypopharynx behind, and the lateral lobes of the thyroid gland, great blood vessels, and nerves on both sides.
The larynx of adults is located in front of the 3rd to 6th cervical vertebrae
cartilage
Thyroid cartilage
The largest area
structure
Front angle: A forward longitudinal bulge formed where the front edges of the two plates meet.
Adam's apple: the forward protrusion of the upper end of the forefoot of the thyroid cartilage
Upper and lower corners: a pair of protrusions extending upward and downward from the rear edges of the left and right plates.
cricoid cartilage
the only complete
epiglottis cartilage
shaped like leaves
arytenoid cartilage
only paired
cartilage connection
joint
cricothyroid joint, cricoarytenoid joint
elastic cone
Median cricothyroid ligament
Puncture can be performed here
Vocal cords: vocal ligaments, vocal cord muscles, vocal clefts (can adjust the pitch of the voice)
laryngeal muscles
It is the power organ of our pronunciation. It is mainly striated muscle and belongs to skeletal muscle.
It has the function of tensing and relaxing the vocal cords, enlarging and narrowing the glottis cleft and narrowing the larynx.
laryngeal cavity
The laryngeal cavity is a tube cavity surrounded by laryngeal cartilage, laryngeal muscles, laryngeal mucosa, ligaments, fibrous membrane, etc.
The laryngeal cavity starts from the mouth of the larynx and communicates with the pharynx; downwards it passes through the trachea and connects to the bronchi and lungs.
three parts
The laryngeal cavity is bounded by the planes of the vestibular and glottal fissures.
laryngeal vestibule
middle cavity of larynx
subglottic cavity
Two splits
Vestibular fissure: the cleft between the two vestibular folds
Glottic cleft: the narrowest part of the larynx
The larynx is the upper opening of the hypopharynx and is bounded by the upper edge of the epiglottis, the aryepiglottic folds and the interarytenoid notch.
trachea and bronchi
trachea
It originates from the lower edge of the cricoid cartilage, goes down to the sternal angle plane, and bifurcates to form the left and right main bronchi.
Divided into tracheocervical and tracheothorax
The tracheal cartilage is composed of 14-17 C-shaped notched posterior hyaline cartilage rings.
Tracheostomy is often performed at the 2nd to 4th tracheal cartilages.
tracheal bifurcation
bifurcation of left and right main bronchi
tracheal carina
Slightly to the left, which is an important criterion for judging tracheal bifurcation during bronchoscopy.
bronchi
Left main bronchus: long, thin, and horizontal
Right main bronchus: short, thick, steep. Many foreign objects fall here
pleura
definition
Lining the inner surface of the chest wall, above the septum, both sides of the mediastinum, and the surface of the lungs. Divided into parietal pleura and visceral pleura
chest
The total cavity bounded by the thorax and diaphragm.
parietal pleura
Costal pleura: Covers the inner part of the chest wall
Diaphragmatic pleura: covering the upper part of the diaphragm
Mediastinal pleura: the part covering both sides of the mediastinum
pleural roof
costophrenic recess
intercostal recess, intercostal recess, septal mediastinal recess
Body surface projection of pleura and lungs
mediastinum
definition
A general term for all organs and tissue structures between the mediastinum and pleura on both sides
Location
The mediastinum is slightly to the left, narrow above and wide below.
branch
Bounded by the horizontal plane of the sternal angle
superior mediastinum
inferior mediastinum
bounded by pericardium
anterior, middle, posterior mediastinum
lung
Located in the chest, above the septum, on both sides of the mediastinum, one on each side
form
A sharp point
Lung apex - blunt and round, protrudes into the base of the neck through the thorax, 2 to 3 cm above the inner 1/3 of the clavicle.
bottom
Lung base (diaphragm surface) - close to the diaphragm, sunken upward
Three sides
The three sides adjacent to the lungs
rib surface
Located on both sides adjacent to ribs
next door
Next to the partition
mediastinum
adjacent to mediastinum
hilum
The central depression on the medial surface is the portal for the entry and exit of the main bronchi, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels and nerves.
lung root
The structures entering and exiting the hilum are surrounded by connective tissue.
Arrangement of structures
from front to back
pulmonary veins, pulmonary arteries, bronchi
from top to bottom
left lung
Pulmonary artery, bronchus, pulmonary vein
right lung
bronchi, pulmonary artery, pulmonary vein
color
red
pulmonary veins, internal arterial blood
blue
Pulmonary artery, internal venous blood flow
White
bronchi
Three fates
Front edge: sharp and thin, with a heart notch on the lower part of the front edge
Trailing edge: blunt rounded
Lower edge: sharper
Lobulation
left lung
Divided into upper and lower leaves by oblique lobes
right lung
It is divided into upper, middle and lower lobes by the oblique fissure and the horizontal fissure of the right lung.
The difference between fetal lungs and adult lungs
Adult lungs can surface
bronchopulmonary segment
Clinically, the bronchopulmonary segment can be used as the location for surgical resection.
pharynx
see digestive system
Summary
constitute
respiratory tract
Upper respiratory tract
nose, pharynx, larynx
lower respiratory tract
trachea, bronchi
lung
lung parenchyma
bronchial tree and alveoli
interstitium
Connective tissue, blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, nerves
Function
It mainly carries out gas exchange, as well as smell, pronunciation, neuroendocrine function, assists in the return of venous blood to the heart, and participates in the metabolism of certain substances.
The alveoli are the final site for gas exchange