MindMap Gallery Medical Imaging Respiratory Disease Diagnosis
- 41
Medical Imaging Respiratory Disease Diagnosis
Medical imaging: mind map for diagnosis of respiratory diseases, including bronchiectasis, pneumonia, tuberculosis, lung tumors, and mediastinal tumors.
Edited at 2024-04-06 17:40:07- 30 Creative Ideas for Valentine's Day
This Valentine's Day map illustrates love through 30 romantic possibilities, from the vintage charm of "handwritten love letters" to the urban landscape of "rooftop sunsets," from the tactile experience of a "pottery workshop" to the leisurely moments of "wine tasting at a vineyard"—offering a unique sense of occasion for every couple. Whether it's cozy, experiential, or luxurious, love always finds the most fitting expression. May you all find the perfect atmosphere for your love story.
- Milano Cortina 2026 Ice Hockey Schedule
The ice hockey schedule for the Milano Cortina 2026 Winter Olympics, featuring preliminary rounds, quarterfinals, and medal matches for both men's and women's tournaments from February 5–22. All game times are listed in Eastern Standard Time (EST).
- 2026 Personal Annual Planning Handbook
This 2026 planner effectively combines goal setting with practical tools, including monthly plans, weekly plans, and monthly reviews. Integrated lifestyle and leisure sections ensure work-life balance, while the quarterly layout provides a clear structure for tracking progress. The planner's simple and clear design helps you clarify your goals, cultivate habits, and cherish every important moment – turning your plans into reality step by step, with new achievements every week.
Medical Imaging Respiratory Disease Diagnosis
- 30 Creative Ideas for Valentine's Day
This Valentine's Day map illustrates love through 30 romantic possibilities, from the vintage charm of "handwritten love letters" to the urban landscape of "rooftop sunsets," from the tactile experience of a "pottery workshop" to the leisurely moments of "wine tasting at a vineyard"—offering a unique sense of occasion for every couple. Whether it's cozy, experiential, or luxurious, love always finds the most fitting expression. May you all find the perfect atmosphere for your love story.
- Milano Cortina 2026 Ice Hockey Schedule
The ice hockey schedule for the Milano Cortina 2026 Winter Olympics, featuring preliminary rounds, quarterfinals, and medal matches for both men's and women's tournaments from February 5–22. All game times are listed in Eastern Standard Time (EST).
- 2026 Personal Annual Planning Handbook
This 2026 planner effectively combines goal setting with practical tools, including monthly plans, weekly plans, and monthly reviews. Integrated lifestyle and leisure sections ensure work-life balance, while the quarterly layout provides a clear structure for tracking progress. The planner's simple and clear design helps you clarify your goals, cultivate habits, and cherish every important moment – turning your plans into reality step by step, with new achievements every week.
- Recommended to you
- Outline
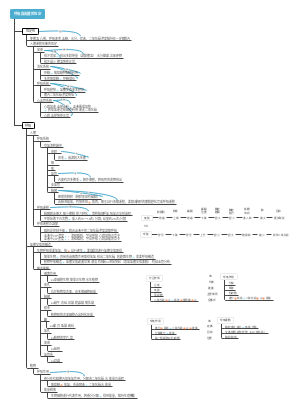
Respiratory disease diagnosis
bronchiectasis
Irreversible abnormal enlargement of bronchial diameter
More common in children and young adults
Lower lobes of both lungs, lingual segment of left lung, middle lobe bronchus of right lung
Cough, expectoration of purulent sputum, hemoptysis
CT
Column type - orbital sign, signet ring sign
Varicose type - rosary shape
Cystic type - grape cluster shadow
Mucus plug - rod-shaped, nodular high-density shadow, finger-like sign
pneumonia
Lobar pneumonia
Young adults, winter and spring
Sudden onset, chills, high fever, chest pain, and rust-colored phlegm
Increased white blood cell count, increased neutrophil count
CT
Hyperemic period - ground glass shadow with blurred edges
Red and gray liver degeneration stage - dense consolidation, "air bronchogram"
Dissipation period - scattered shadows
Lobular pneumonia (bronchopneumonia)
Infants, the elderly, postoperative complications
Lobular bronchi, spreading to adjacent
Fever, cough, mucus sputum, chest pain, dyspnea, and cyanosis
X-ray
The middle and lower fields of both lungs, the inner middle zone
Scattered patchy shadows with blurred edges; increased and blurred lung textures
CT
Nodular shadows and patchy shadows of varying sizes and blurred edges
Lobar bronchial obstruction—lobular emphysema, atelectasis
interstitial pneumonia
infants
Infiltration of inflammatory cells in the walls of small bronchial tubes and interstitium of lungs
Fever, cough, shortness of breath, cyanosis
X-ray
Naka Shimono
The lung texture is thickened and blurred - reticular and small patchy shadows
Increased hilar density and unclear structure
lung abscess
Pathogens - necrotizing inflammatory diseases
Direct spread of inhalation, blood-borne, and adjacent organ infections
Sudden onset, chills, high fever, chest pain, coughing up pus and smelly sputum, and increased white blood cell count
——Chronic: cough, purulent sputum, bloody sputum, irregular fever, anemia, weight loss, clubbing of fingers/toes
X-ray
Single/multiple (hematogenous)
Globular shadow, thick-walled cavity, smooth inner wall, gas-liquid plane
Acute - blurry oozing shadow around cavity wall Chronic - the cavity has thin walls, narrowed cavity, and surrounding disordered cord-like fibrous lesions
CT
Enhancement - the abscess wall is significantly enhanced
tuberculosis
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, chronic infectious disease
(Early stage) excessive bacteria and low immunity - exudation (serous/cellulosic); Few bacteria and strong immunity - proliferative lesions (tuberculous granuloma); Excess bacteria, low immunity, obvious allergic reactions/without appropriate treatment - develop into necrotic lesions (caseous changes)
Treatment - Lesion resorption, fibrosis, calcification; Progress - Expansion, Dissolution, Liquefaction, Hollow - Spread
Types
Primary tuberculosis (type I)
children, teenagers
X-ray
"Dumbbell"
Primary infiltrative focus——Nakageno
Lymphangitis - primary tumor moves toward the hilus
Enlargement of hilar and mediastinal lymph nodes
CT
Enhancement—circular enhancement of lymph nodes (central caseous necrosis)
Hematogenous disseminated pulmonary tuberculosis (type II)
acute
X-ray/CT
Diffuse miliary shadow
Three uniformities: uniform distribution, uniform size, uniform density
subacute, chronic
Small and frequent hematogenous dissemination
X-ray/CT
Three non-uniformities: different sizes, unequal densities, and uneven distribution
Secondary pulmonary tuberculosis (type III)
adult
Including infiltrative tuberculosis, tuberculosis, caseous pneumonia, fibrocavitary tuberculosis
Infiltrative pulmonary tuberculosis (main signs)
Localized patchy shadows—apical segments, posterior segments of upper lobes, and dorsal segments of lower lobes of both lungs
lobar caseous pneumonia
Large areas of dense consolidation with irregular “worm-eaten” cavities inside and blurred edges
proliferative disease
Spot-like shadow, clear edge, "plum petal"/"tree bud sign"
tuberculosis balls
Round, oval, clear edges, smooth outline
Occasionally there are lobes, and there may be calcification inside
Surrounding "satellite stoves"
Tuberculous cavities
Thin wall, smooth inner and outer edges, "satellite stove"
Bronchial disseminated disease
Patchy shadows distributed along the bronchi/"tree-in-bud sign"
Interstitial changes in the lungs
Fine mesh-like linear shadows and micronodules in the leaflets, "tree-bud sign"
Ground glass shadow, interlobular septal thickening, airway wall thickening
Indurated calcification/cord shadow
Prompts healing of lesions
Fibrocavitary tuberculosis
late type
Tuberculosis lesions linger and fail to heal, destroying lung tissue - fibrous cavities
X-ray/CT
Fiber cavity: upper middle field, thick wall, smooth inner wall
Changes around the cavity: large exudates, caseous lesions, varying degrees of calcification, and a large number of fibrotic lesions
Lung lobe deformation: lung lobe shrinkage, affected side hilum lifted, lung texture disordered, "weeping willow-like"
Compensated emphysema: non-diseased lung compensation
Pleural hypertrophy and adhesions
Mediastinal shift to the affected side
Tuberculous pleurisy (type IV)
Dry Exudative - pleural effusion, serous/bloody
Directly invades the pleura/travels through lymphatic vessels/menstrual blood
X-ray/CT
Pleural effusion of varying degrees
Chronic—extensive/localized thickening with pleural calcification
Extrapulmonary tuberculosis (type V)
bacterium-negative pulmonary tuberculosis
Diffuse Lung Disease (DLD)
idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
X-ray/CT: Early stage - ground glass shadow Progressive stage - diffuse reticular/small nodular shadow Late stage - diffuse multiple cystic radiolucent shadows, "honeycomb lung"
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP)
insoluble phospholipid-rich protein
X-ray: Diffuse ground glass shadow - patchy shadow, fused consolidation shadow, "air bronchus sign" and "butterfly wing"
CT: "Map-like" - clear boundaries between the lesion and surrounding tissue Interlobular septal thickening, ground glass density shadow - "gravel road" look
lung tumor
Small cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma, large cell carcinoma
Original hairstyle
central type
Peripheral type
Diffuse type
Secondary hair
Blood flow
lymphatic tract
spread directly
central type
direct signs
Intrabronchial/intra-mural soft tissue mass
Irregular pipe walls
Luminal stenosis/truncation
indirect signs
Obstructive pneumonia—consolidation of lung tissue distal to the affected bronchus
Atelectasis - the uniform density of lung lobes or lung segments increases and the volume decreases
CT enhancement - uneven enhancement
Reverse "S" sign: right hilar mass accompanied by atelectasis of the right upper lung, composed of the mass and the lower edge of the atelectatic lung.
Peripheral type
direct signs
Spiculum sign, lobulation sign, air bronchial sign, vacuole sign, bronchovascular bundle sign, pleural depression sign, calcification
indirect signs
Metastasis, pleural effusion
When lung adenocarcinoma is small - ground glass nodules (pure ground glass nodules, mixed ground glass nodules)
Cancerous cavities—thick-walled eccentric cavities
Diffuse type
Widely distributed nodules and enlarged hilar/mediastinal lymph nodes
"Air bronchogram" walking stiffness
mediastinal tumors
Classification
Anterior mediastinum: intrathoracic goiter, thymoma, teratoma
Middle mediastinum: lymphoma, bronchial cyst
Posterior mediastinum: neurogenic tumors
Intrathoracic goiter: CT - density is higher than soft tissue, can become cystic/calcified (may have symptoms of hyperthyroidism)
Thymoma: middle and upper part of anterior mediastinum. Over 30 years old
Invasiveness - unclear margins, uneven density Non-invasive
Teratoma: middle anterior mediastinum
Cystic (dermoid cyst) – 2 germ layers (middle and outer)
Solid – 3 germ layers (hair, teeth, bones, glands)
Lymphoma: Anterior and middle mediastinum
X-ray - the mediastinum widens to both sides, and the edges are wavy
CT - lymph nodes are enlarged and show uniform soft tissue density; Enhance - moderately enhanced
Neurogenic tumors: Posterior mediastinum - round/"dumbbell-shaped"
CT: Uniform soft tissue density shadow, smooth edges, possible calcification/cystic changes
Malignant - may be accompanied by massive calcification, pyramidal bone destruction, and adjacent soft tissue involvement
cystic mass
No reinforcement
oppression of surrounding tissues
Superior vena cava - thickened jugular vein, edema of head, neck, face and upper limbs
Trachea - irritating dry cough, shortness of breath
Phrenic nerve - hiccups, diaphragmatic paralysis
Sympathetic nervous system - Horner syndrome
Vagus nerve - decreased heart rate, nausea, vomiting
Recurrent laryngeal nerve - hoarseness
Esophagus - difficulty swallowing