MindMap Gallery Internal Medicine Chapter 01 Respiratory System Section 01
- 56
Internal Medicine Chapter 01 Respiratory System Section 01
The self-used mind map of the Western Comprehensive Examination for the Postgraduate Entrance Examination is focused. Although it is not flashy, it is absolutely practical. It integrates the key points of other postgraduate entrance examination teachers such as Tianying, Senior Brother Tiantian and Lao He. It can also be convenient for users to modify by themselves. It also comes with postgraduate examination questions. Some classic or difficult questions that I encountered during the process can be easily consolidated by reading and doing them. I also added some memory techniques and memory tips found in the comment area of the questions to reduce the difficulty of memory for users.
Edited at 2024-04-03 12:59:56- 30 Creative Ideas for Valentine's Day
This Valentine's Day map illustrates love through 30 romantic possibilities, from the vintage charm of "handwritten love letters" to the urban landscape of "rooftop sunsets," from the tactile experience of a "pottery workshop" to the leisurely moments of "wine tasting at a vineyard"—offering a unique sense of occasion for every couple. Whether it's cozy, experiential, or luxurious, love always finds the most fitting expression. May you all find the perfect atmosphere for your love story.
- Milano Cortina 2026 Ice Hockey Schedule
The ice hockey schedule for the Milano Cortina 2026 Winter Olympics, featuring preliminary rounds, quarterfinals, and medal matches for both men's and women's tournaments from February 5–22. All game times are listed in Eastern Standard Time (EST).
- 2026 Personal Annual Planning Handbook
This 2026 planner effectively combines goal setting with practical tools, including monthly plans, weekly plans, and monthly reviews. Integrated lifestyle and leisure sections ensure work-life balance, while the quarterly layout provides a clear structure for tracking progress. The planner's simple and clear design helps you clarify your goals, cultivate habits, and cherish every important moment – turning your plans into reality step by step, with new achievements every week.
Internal Medicine Chapter 01 Respiratory System Section 01
- 30 Creative Ideas for Valentine's Day
This Valentine's Day map illustrates love through 30 romantic possibilities, from the vintage charm of "handwritten love letters" to the urban landscape of "rooftop sunsets," from the tactile experience of a "pottery workshop" to the leisurely moments of "wine tasting at a vineyard"—offering a unique sense of occasion for every couple. Whether it's cozy, experiential, or luxurious, love always finds the most fitting expression. May you all find the perfect atmosphere for your love story.
- Milano Cortina 2026 Ice Hockey Schedule
The ice hockey schedule for the Milano Cortina 2026 Winter Olympics, featuring preliminary rounds, quarterfinals, and medal matches for both men's and women's tournaments from February 5–22. All game times are listed in Eastern Standard Time (EST).
- 2026 Personal Annual Planning Handbook
This 2026 planner effectively combines goal setting with practical tools, including monthly plans, weekly plans, and monthly reviews. Integrated lifestyle and leisure sections ensure work-life balance, while the quarterly layout provides a clear structure for tracking progress. The planner's simple and clear design helps you clarify your goals, cultivate habits, and cherish every important moment – turning your plans into reality step by step, with new achievements every week.
- Recommended to you
- Outline
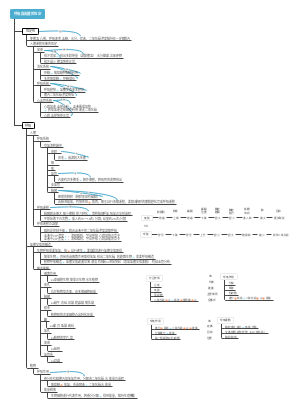
Internal Medicine Chapter 01 Respiratory System Section 01
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
concept
"Persistent airflow limitation", mainly expiratory dyspnea, is a manifestation of increased small airway resistance and airway narrowing
In the early stage, the flow volume curve can be used to indicate the presence of early small airway lesions.
Cause
①Smoking
Smoking→Chronic bronchitis→Emphysema→COPD
Emphysema
终末支气管气腔出现异常扩张,伴有肺泡破坏
肺泡活性物质缺乏会加重肺气肿,但不会引起肺气肿
分类
中央型肺气肿
一般由吸烟引起
周围型肺气肿
全小叶型肺气肿
由抗蛋白酶系统失衡引起,全肺弹性蛋白破坏,所以全小叶都有肺气肿
②Infection
The most important factors for acute exacerbation
Lower respiratory tract infections in childhood can also cause COPD
③Imbalance between protease and anti-protease systems
The elastin of the airway wall is destroyed, resulting in a decrease in elastic resistance and expiratory dyspnea; And increased lung compliance can lead to barrel chest
Congenital alpha₁-antitrypsin deficiency can lead to lung tissue destruction and cause emphysema But more common in Northern European ancestry
pathology
The combined manifestations of chronic bronchitis and emphysema are mainly persistent airflow limitation
Pathogenesis
①Respiratory bronchiolar stenosis
②Excessive expansion of the air cavity
③Destruction of air cavity wall
Note, there is no "pulmonary fibrosis"
Clinical manifestations [postgraduate entrance examination focus]
symptom
Coughing up phlegm and shortness of breath
Coughing up phlegm and shortness of breath are synonymous with COPD.
①Repeated cough
② Coughing up phlegm
③Wheezing
④Shortness of breath after activity (signature symptom)
physical signs
Inspection
barrel chest
palpation
Bilateral voice tremor is weakened (because there is too much air and water in the lungs, and the pleura is thicker)
percussion
The lungs are too unvoiced, the heart dullness boundary is narrowed, and the liver dullness boundary is decreased.
widening of kronig gorge
Emphysema and COPD result in widening of the Kronig isthmus And tuberculosis is the narrowing of Kronig's Gap
auscultation
Reduced breath sounds and prolonged expiratory phase Dry rales and dry and wet rales can be heard coexisting
Auxiliary inspection
①Pulmonary function test (gold standard)
Demonstrated persistent airflow limitation
Pulmonary function tests
考研中有2个病一定要做肺功能检查
COPD和支气管哮喘
检查方式
吸入支气管扩张剂后,FEV₁/FVC<70%,说明有持续性气流受限,正常人是83%
②X-ray
The brightness of both lung heads increases (there is too much air), and the intercostal space becomes wider, but there is no obvious change in the early stage.
③TLC (total lung capacity), FRC (functional residual capacity), RV (residual capacity) increase, while VC/FVC decreases
④The dynamic compliance of the lungs decreases and the static compliance increases
The elastic components of the lungs are massively destroyed → the elastic resistance of the lungs decreases → the static compliance of the lungs increases Bronchioles are blocked and negative thoracic pressure decreases→airway resistance increases→pulmonary dynamic compliance decreases
diagnosis
Preferred pulmonary function test
After inhaled bronchodilator, one second rate FEV₁/FVC < 70%
Diagnosis of clinical manifestations
Smoking, usually no hemoptysis, shortness of breath and expectoration, most likely COPD
COPD complicated by pneumothorax
X-ray is preferred
When COPD is complicated by heart disease
Preferred blood gas analysis
Complications [three major complications to remember]
①Pulmonary heart disease
Symptoms of right ventricular insufficiency, edema of both lower limbs, etc.
②Type II respiratory failure (PaO₂<60, PCO₂>50)
COPD is the most important cause of type II respiratory failure, mainly caused by decreased alveolar ventilation.
③Spontaneous pneumothorax
reason
There is too much gas in the lungs. If the pleura ruptures when coughing, pneumothorax will occur.
symptom
The patient first experienced sudden chest pain and then developed dyspnea.
Pneumothorax and pulmonary embolism
气胸与肺栓塞是难兄难弟,考试永远在一块儿,不好区分 气胸是先有胸痛,后有呼吸困难,有先有后; 肺栓塞的胸痛和呼吸困难没有先后之分
treat
X-rays and EKGs, and general supportive care
If you have a lot of underlying diseases and difficulty breathing, sedatives cannot be used to avoid suppressing breathing.
If there is no impairment of consciousness, mechanical ventilation is generally not required
treat
① Anti-infection [key treatment 1]
Prevent acute exacerbations
②Asthma [Key Treatment 2]
Bronchodilators
③Relieves cough and resolves phlegm
For patients with thick sputum
④ Oxygen inhalation
Continuous low-concentration and low-flow oxygen inhalation (30% oxygen, 1~2L/min)
Replenish
Bronchodilators
Divided into beta-agonists and M-receptor blockers
beta agonist
Short-acting (SABA): albuterol
Long-acting (LABA): formoterol
M receptor blockers
Short-acting (SAMA): ipratropium bromide
Long-acting (LAMA): tiotropium bromide
The mechanism of O₂ deficiency and CO₂ retention in COPD
① Ventilatory dysfunction and reduced alveolar ventilation (main reason)
② Ventilation dysfunction
V/Q imbalance (mainly leading to hypoxia, and in severe cases, CO₂ retention)
Impaired diffusion (resulting in hypoxia)
③Intrinsic positive end-respiratory pressure (PEEP)
Smoking causes neutrophil activation and damages pulmonary elastic fibers → difficulty in expiration → increased alveolar residual air at the end of expiration → intrapulmonary pressure is greater than atmospheric pressure, resulting in long-term exertion of respiratory muscles → respiratory muscle fatigue
Assessment of disease severity during stable phase [newly added test questions]
Pulmonary function assessment
The first thing to check is whether it is COPD, so first we need to check FEV₁/FVC Then we need to look at the size of FEV₁/predicted value, which is used to classify the severity.
Notice
分度的时候,是看FEV₁/预计值,而不是FEV₁/FVC
Graduation
Mild (Level 1)
FEV₁/predicted value ≥80%
Moderate (Level 2)
FEV₁/expected value is between 50% and 79%
Severe (Level 3)
FEV₁/expected value is between 30%~49%
Extremely severe (level 4)
FEV₁/predicted value<30%
358 divisions
mMRC classification
Few symptoms
Level 0
Difficulty breathing during strenuous activity
Level 1
Difficulty breathing when walking briskly on level ground or climbing walls
[Difficulty breathing when walking strenuously, briskly, or climbing, but no need to rest]
Many symptoms
level 2
Due to difficulty breathing, I need to stop and rest while walking on level ground.
Level 3
You need to stop and rest after walking 100 meters or a few minutes on level ground.
level 4
Severe difficulty breathing or being unable to leave home, or difficulty breathing when putting on or taking off clothes
[Need to stop and rest]
Group
Group A
Low risk, number of acute exacerbations in the past year ≤ 1, MRC grade ≤ 1, use SAMA or SABA treatment
Group B
Low risk, with ≤1 exacerbation in the past year, MRC grade ≥2, treated with LAMA or LABA
Group C
High risk, number of acute exacerbations in the previous year ≥ 2, MRC grade between 0 and 1, use LAMA, or LAMA LABA, or ICS LABA treatment
Groups C and D both use combination drugs
Group D
High risk, the number of acute exacerbations in the past year is ≥2, and the MRC grade is ≥2, use LAMA LABA, or add ICS treatment
Treatment of acute exacerbations
Acute COPD classification
Level I
No respiratory failure or altered unconsciousness
Level II
Respiratory failure, altered unconsciousness
Level III
Have respiratory failure, altered state of consciousness
treat
①Treat the primary disease, such as infection
②Inhaled bronchodilators
③Oral or intravenous glucocorticoids, expectorant, and mechanical ventilation if necessary
When PaO₂<40 or PaCO₂>70, perform mechanical ventilation Non-invasive mechanical ventilation for unconscious disorders Invasive mechanical ventilation for patients with impaired consciousness
Note before use: ①Contents framed with “[]” and “[]” are generally memory techniques and memorization formulas. ② I have divided different diseases in the same chapter to make it easier for users to view mind maps, so there will be many mind maps. You can go to my homepage to find them. ③The mind map is still being updated. In order to prevent misleading users, I am still modifying it, so some chapters have not been released yet. I hope you can forgive me if there are any errors.
pulmonary embolism
concept
A group of diseases in which various emboli block the pulmonary arteries and their branches
acute pulmonary thromboembolism
concept
Differentiation between pulmonary embolism and pulmonary thrombosis
Pulmonary embolism: an emboli formed elsewhere travels to the pulmonary artery, mainly from deep vein thrombosis of the lower limbs Pulmonary thrombosis: emboli that form in situ in the lungs
risk factors
① Vascular endothelial injury (most important)
Trauma/fracture, smoking, arteriovenous puncture [These 3 reasons must be remembered, I have taken the test many times]
② Blood stasis
Bedridden for a long time
③ Hypercoagulable state of blood
Age (an independent risk factor)
Pathophysiology [very important]
Increased ventilation/blood flow ratio → pulmonary ventilation dysfunction → hypoxia → type I respiratory failure
Clinical manifestations [very important]
"Two major symptoms and two major signs"
Two major symptoms
Sudden chest pain, difficulty breathing (shortness of breath)
Two major signs
① Hyperactive second heart sound (P₂) in pulmonary valve area → Pulmonary hypertension ②Jugular venous distension → right atrial hypertension
triad of pulmonary embolism
Sudden chest pain, hemoptysis, difficulty breathing, but only seen in 20% of patients
Auxiliary inspection
①Blood D-dimer
Elevated D-dimer represents hyperfibrinolysis and indicates thrombosis. D-dimer positivity does not diagnose pulmonary embolism Negative D-dimer can rule out pulmonary embolism
Therefore, it is mainly used to screen for the possibility of pulmonary embolism. <500ug/L, pulmonary embolism can be ruled out
②Arterial blood gas analysis
PaO₂↓, PaCO₂↓ (tachypnea, hyperventilation, PaCO₂↓), pH↑
③CTPA (preferred examination)
CT pulmonary angiography is a non-invasive examination and is the preferred examination for pulmonary embolism (filling defect)
④ Radionuclides [passed the postgraduate entrance examination]
Great diagnostic value for pulmonary embolism
⑤Pulmonary angiography DSA
The gold standard for pulmonary embolism
The gold standard for vascular diseases is generally angiography DSA
Treatment[Key]
①General treatment
Bed rest, nasal cannula for oxygen
②Anticoagulation and thrombolytic therapy
Types
Summary routine
血压低,我溶栓; 血压正常我抗凝
High risk type (large area)
①Echocardiography shows decreased right ventricular function ②Low blood pressure
The preferred anticoagulant therapy is mainly thrombolytic therapy
Medium risk type (sub-large area)
①Echocardiography shows decreased right ventricular function ②Normal blood pressure
Preferred anticoagulant therapy Uncertain about thrombolysis
Low risk type (not large area)
①Echocardiogram shows normal right heart function ②Normal blood pressure
Anticoagulant therapy is preferred; thrombolytic therapy is not suitable
anticoagulant therapy
drug
Low molecular weight heparin (preferred), warfarin (need to overlap with heparin for more than 5 days)
Course of treatment
① Risk factors can be eliminated in the short term (such as surgery, taking estrogen or temporary immobilization) - → 3 months
②First case of unknown source of emboli—→6 months
③ Recurrence of thrombosis and long-term presence of risk factors—→12 months or lifelong
Thrombolytic therapy
drug
rt-PA, urokinase, streptokinase
Time Window
Within 14 days
Exam questions
伴有血流动力学紊乱的,大面积肺栓塞的溶栓治疗,其时间窗是≤14天
对,反正就是14天,如有新发的情况可以延长
Absolute contraindications to thrombolysis
intracranial hemorrhage
But even if there is a history of intracranial hemorrhage, thrombolysis is still necessary for high-risk patients
Replenish
Pulmonary function tests show obstructive ventilatory dysfunction
①COPD
②Bronchiolitis obliterans
③Diffuse panbronchiolitis
④Bronchiectasis
Various respiratory symptoms
acute pleurisy
suppressed breathing
acidosis
kussmaul breathing
nervous
Breathing rate is fast and shallow
neurogenic dyspnea
Sobbing breathing
psychogenic dyspnea
Sighing breathing
cerebral hemorrhage
pause in breathing
Morphine, barbiturates, organophosphate poisoning
Intermittent breathing (biots breathing)
drug
Morphine and other central antitussives are contraindicated in respiratory diseases
Diazepam and other sedatives are contraindicated in disorders of consciousness
Most acidosis caused by respiratory diseases does not require alkali supplementation, and alkali supplementation is required only when the pH is <7.2.
3 common diagnostics of exclusion
BNP
Rule out heart failure
D-dimer
Rule out pulmonary thromboembolism
ANA
Exclude SLE
Exam questions
Diseases that can be diagnosed with radionuclides are
pulmonary embolism
In case of pulmonary embolism, the most important thing to take thrombolytic treatment is
Blood pressure and right heart function
The time window for pulmonary embolism thrombolytic treatment is
≤14 days
Signs of chronic bronchitis may appear
bubble sound
Correct, vesicular sounds are produced by the rupture of secretion vesicles in the respiratory tract. Chronic bronchitis has strong mucus secretion, so there are vesicular sounds.
wheeze
Correct, wheezing occurs when the airway is narrowed and blocked. The gas passes through to form turbulent flow. The fibrous tissue around the bronchus proliferates and the airway is narrowed, so there is wheezing.
The pathogenesis of emphysema is that chronic inflammation destroys the alveolar interstitium, causing it to lose its stent function and promoting alveolar expansion.
mistake First, obstructive emphysema does not have obvious pulmonary fibrosis, so the interstitium of the lungs will not change. Second, it is not the alveolar interstitium that is damaged, but the alveolar cavity is enlarged and ruptured, and the alveolar walls are damaged.
Pulmonary fibrosis is involved in the pathogenesis of obstructive emphysema
Wrong, has nothing to do with pulmonary fibrosis
Hypoxemia occurs in patients with COPD. The main mechanism is imbalance of ventilation-blood flow ratio.
Wrong, the main reason is the decrease in alveolar ventilation
Kronig's Gap is when the upper boundary of the lungs is percussed. The normal percussion sound at the lung apex is voiceless, with a width of about 5cm. It is called Kronig's Gap. Kriong's Gap changes in the following diseases:
Emphysema
Kronig Gorge widens
tuberculosis
Kronig narrows
pneumonia
no significant changes
pleural effusion
no significant changes